On Monday, the White House Council of Economic Advisers (CEA) released a report examining the long-term decline in the share of prime-age men (aged 25 to 54) who are either working or actively looking for work. What economists call the labor force participation rate for this population decreased from 98 percent in 1954 to 88 percent today, the second largest decrease among OECD countries. This trend has raised concerns not only for its impact on economic growth, but also because it seems to track an increase in mortality over that time, particularly among white males, as economists Anne Case and Angus Deaton have found.
The CEA report documents a number of possible explanations for this trend, including increasing rates of women in the workforce, rising disability insurance claims, falling demand for less-skilled workers, and barriers to employment for those with criminal records.
The report’s national analysis alone, however, obscures tremendous variation across the United States in employment among this critical group.
According to data from the Census Bureau’s American Community Survey, in 2014, 81 percent of prime-age men nationwide were employed (this statistic differs from the labor force participation rate in that it omits those who are looking for, but not in, work). Yet among the nation’s 374 metropolitan areas for which data are available, that rate ranged from over 93 percent in the oil boomtown of Midland, TX, to just over 50 percent in Kings County in California’s Central Valley.
There are clear regional patterns to this important statistic. Many of the metro areas with the highest employment rates for prime-age men are smaller places located in the middle of the country, from the Upper Midwest, to energy-rich areas in Texas and the Plains states, to the Intermountain West. In several large, economically dynamic metro areas such as Denver, Houston, Minneapolis, San Jose, and Washington, D.C., rates of work among prime-age men are also very high.
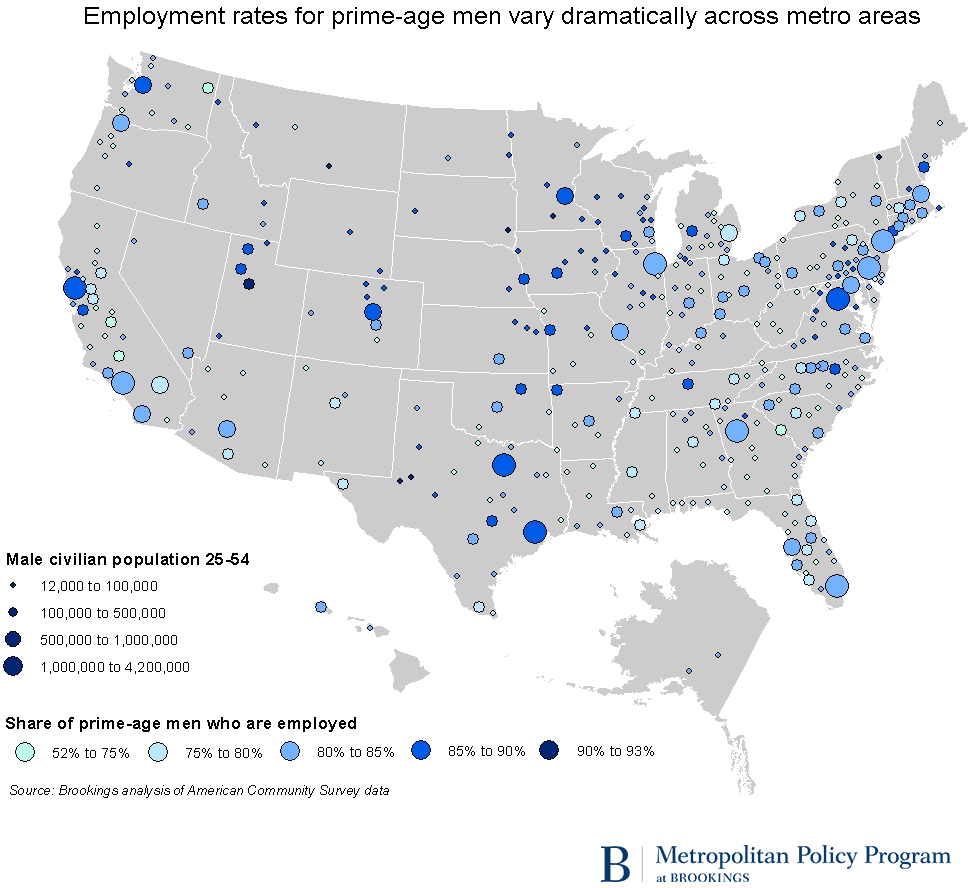
Of much greater concern is the large number of metropolitan regions with very low rates of work among prime-age men. These include many small former industrial centers in states like Michigan, Indiana, and Ohio; areas of West Virginia and Louisiana that rely on declining-employment industries like mining; and long-struggling agricultural economies in Arkansas, Texas, and inland California.
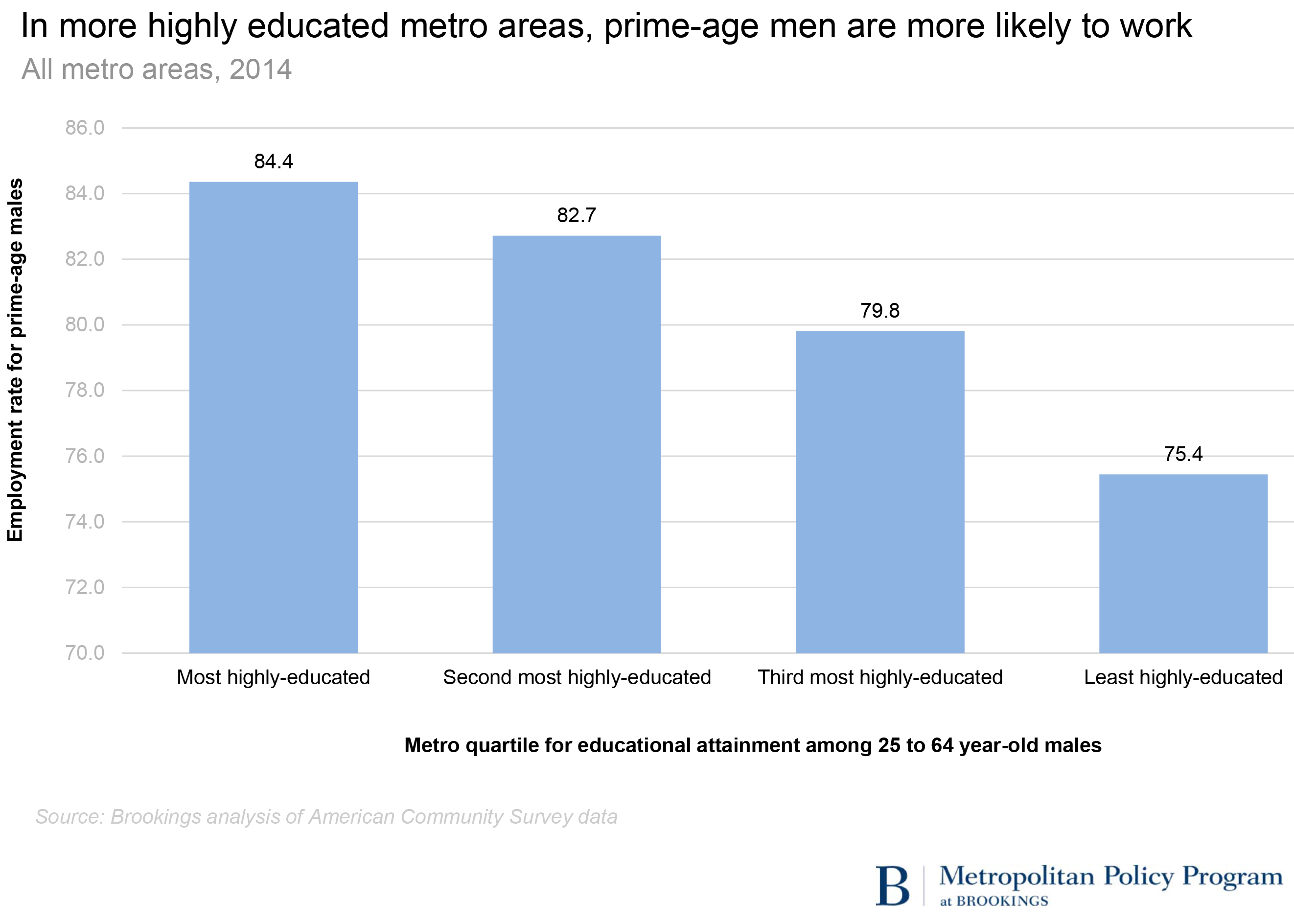
These patterns echo findings from the CEA report that falling demand for labor is an important part of the long-term decline in prime-age male employment. In many places where a high school diploma alone once provided the gateway to a middle-class job, nearly one-third of men in this age group are out of work. This is also evident in the local relationship between educational attainment and work—where educational attainment rates are higher among prime-age men, members of that group are more likely to be employed. A 10-percentage point difference in employment rates separates the most highly-educated quarter of metro areas from the least highly-educated quarter.
Beyond education, size seems to matter, too. Large metro areas exhibit higher rates of work among prime-age men than small metro areas. Across the 100 largest U.S. metro areas, 83.2 percent of prime-age males are employed, compared to 79.8 percent in the smaller 274 metro areas. This relationship partly reflects that men in large metro areas have higher rates of educational attainment than those in small metro areas. Yet even men who have no more than a high-school diploma work at higher rates in large metro areas (64 percent) than similarly educated men in smaller metro areas (62 percent). Larger regional economies with greater economic diversity may stimulate stronger demand for workers at lower skill levels.
Several of the policies that the CEA report recommends to improve prime-age male labor force participation, such as bolstering investment in public infrastructure, reforming unemployment insurance, and boosting educational attainment could help boost rates of work in lagging U.S. metro areas. However, none directly addresses the fact that problems in male employment disproportionately affect small and often economically isolated U.S. regions. This evidence suggests that policies to help dislocated workers relocate to larger, more economically dynamic metro areas—particularly by improving the supply of affordable housing in those regions—should be part of a comprehensive strategy to help reverse the troubling long-term decline in men’s work.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).



Commentary
Where are the nonworking prime-age men?
June 21, 2016