This analysis is part of The Leonard D. Schaeffer Initiative for Innovation in Health Policy, which is a partnership between the Center for Health Policy at Brookings and the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics. The Initiative aims to inform the national health care debate with rigorous, evidence-based analysis leading to practical recommendations using the collaborative strengths of USC and Brookings.
The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015, referred to most often as “MACRA,” set in motion a new approach to Medicare physician payment and replaced the oft-criticized Sustainable Growth Rate with two new payment schemes. In late April, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) released many proposed details surrounding the law’s implementation; however, it is important to keep in mind that the final rule is still forthcoming and may incorporate significant changes in response to public comments made on the proposed rule.
While there are many stakeholders trying to understand the implications of this significant legislation, physicians and other providers—whose response is critical to the success of MACRA—must prepare quickly and almost immediately make decisions about which incentive program to pursue and what steps will increase prospects for success. Starting January 1, 2017, physicians’ and other providers’ performance will determine their payment rate updates. Because of the time required to gather and evaluate performance data, spending and other performance measures in calendar year 2017 will provide the basis for physician payments in 2019.
In this piece, we offer a glimpse into the potential financial changes in physician payment based on the proposed rule. Due to the complexity of the MACRA provisions and their significant effects on payment, policymakers, physicians, and other providers alike must better understand the various dimensions of MACRA. We focus on the financial flow of dollars to help physicians and other providers assess which path within MACRA to take and how best to forecast the impact on their payments, as well as to provide an overview for policymakers on the financial implications of different options physicians are actively weighing now as a result of MACRA.
MACRA overview
As established in the law, MACRA creates two primary payment schemes that physicians accepting Medicare can choose to be judged under:
- The Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS), which administers bonuses or penalties based on how well physicians perform relative to other physicians on a set of quality and value measures (detailed later); or
- The Advanced Alternative Payment Model (APM), which initially offers bonuses and then provides higher annual fee updates than MIPS when physicians earn a sufficient amount of their revenue (or see a sufficient percentage of their patients) through qualifying Medicare or approved private payer payment models that require accepting financial risk if spending exceeds targets.
At least initially, the large majority of physicians and other providers likely will be judged under MIPS, with CMS projecting in the proposed rule that only 4 to 11 percent of Medicare providers will qualify for the Advanced APM payment approach in its first year because of the relatively strict standards to qualify. Unlike the expectations expressed during congressional debate over MACRA, which mainly focused on encouraging physicians to form or contract with APMs, the rules proposed by CMS will lead many to remain in MIPS for the foreseeable future. Indeed, we understand that many physician specialty societies are advising their members to remain in MIPS. In a comment letter to CMS, we suggested ways to better support the pipeline of physicians and other providers into APMs.
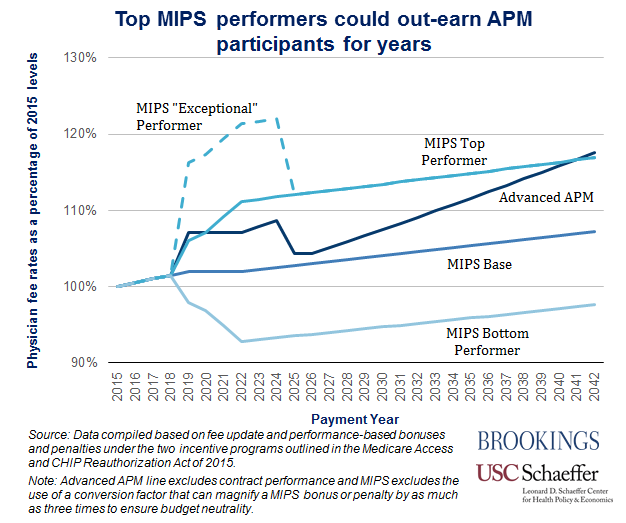
The graph below illustrates the potential scenarios for the flow of funds under the proposed rule. In MIPS, payment is based upon physician performance relative to all other physicians in the program, with bonuses and penalties centered around the base fee-for-service (FFS) payment rates and annual payment updates. MACRA explicitly requires bonuses or penalties in MIPS—not including exceptional performance bonuses—to be budget neutral.
Unlike MIPS, the Advanced APM program dictates that physicians receive a fixed 5 percent bonus for each of the first six years and higher base payment rate updates than MIPS from 2026 onward, in addition to additional bonuses or penalties based on quality and cost performance under their respective Advanced APM contracts. Adding to the contrast with MIPS, bonuses in the Advanced APM program, as well as contractually specified bonuses or penalties, have no requirement to be budget neutral.
The graph below illustrates that consistently high performers in MIPS can actually financially outperform physicians in APMs for many years. In theory, therefore, physicians in an APM—for instance, a Next Generation Accountable Care Organization (ACO)—who are confident that they would score well on relevant quality and value metrics might actually prefer to be judged as a group under MIPS.
In assessing their options, though, it is important to recognize that performance under MIPS as an individual physician or small group may be less predictable than as a part of an APM, because performance in MIPS is relative to the performance of other physicians. This unpredictability occurs because, as explained above, MACRA requires MIPS incentive payments to be budget neutral, which makes performance among MIPS providers a zero-sum-game—one physician’s increase in performance threatens the payment of another, such that bonuses and penalties offset each other overall.
The Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS)
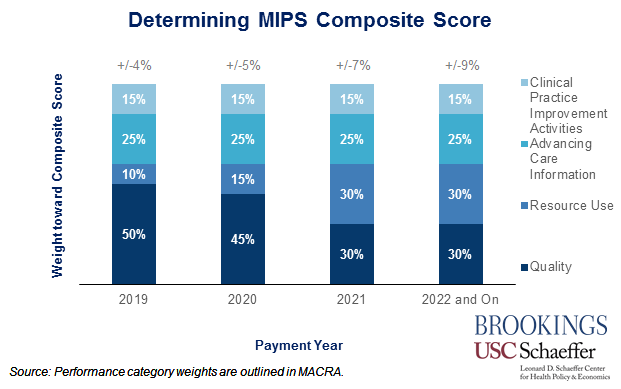
MIPS consolidates three existing programs that dictate physician bonuses or penalties for Medicare physicians and other providers (the physician quality reporting system, a meaningful use incentive program for electronic health record use, and the value-based payment modifier) into a new system that creates a composite score based on:
- The quality of care provided (30 percent in 2021 and beyond), as measured under current law;
- Resource use (30 percent in 2021 and beyond), which consists of the “measures of resource use established for the value-based modifier under current law and, to the extent feasible, accounting for the cost of Part D Drugs”;
- Meaningful use of electronic health records (EHRs) (25 percent), established under current law to determine whether a provider is meaningfully using EHRs; and
- Clinical practice improvement activities (15 percent), a broad subsection decided on by the Secretary.
Physicians and other providers’ weighted scores in each of these categories for a year are aggregated into an overarching Composite Performance Score (CPS) for each practice. The CPS values are ranked from highest to lowest, and the relative ranking of each score determines how provider payments are adjusted, dictating whether a bonus or penalty results as well as its size. Each year, the Secretary will select either the mean or the median of CPSs for that year to serve as the performance threshold above and below which physicians and other providers will receive bonuses or penalties, respectively.
Initially in 2019, 4 percent of a medical professional’s revenue generated through Medicare fee-for-service payments will be redistributed under MIPS, growing to 9 percent by 2022 and remaining at that level indefinitely. By comparison, under the three previous reporting programs, physicians in small practices were subject to combined penalties as high as 6 percent or bonuses up to 2 percent; larger practices (with 8 or more physicians) were subject to maximum penalties and bonuses of 8 percent and 4 percent, respectively.
Maintaining budget neutrality requires that CMS pay the same amount in bonuses as it receives in penalties. To assure that penalties offset bonuses, the MIPS bonus percentages described above are potentially subject to a scaling factor of up to three-times to maintain budget neutrality. For example, having the Secretary adopt the median CPS would mean half of all physician practices would rank above that value and half would rank below. However, because practices can differ in both number of physicians and the extent of their Medicare billing, there is no guarantee that the Medicare payments—and associated bonuses—earned by practices above the midpoint would exactly equal the penalties owed by practices below the midpoint. CMS would compute and apply an appropriate scaling factor to assure total bonuses equal total penalties and achieve budget neutrality.
Outside of the budget neutrality requirement, the law provided $500 million each year from 2019 to 2024 to award “exceptional performance” bonuses to MIPS providers with the highest composite performance scores. The bonuses would be awarded on a sliding scale up to as high as 10 percent added to the base MIPS bonus.
Advanced Alternative Payment Models (Advanced APMs)
The other pathway under MACRA involves alternative payment models that meet the criteria established by CMS to be designated “advanced.” Advanced APMs are defined as (i) measuring physicians and other providers according to metrics similar to those of MIPS, (ii) requiring providers’ use of certified EHRs, and (iii) holding providers accountable for at least “nominal financial risk.” In the proposed rule, CMS outlines which of its current APMs measure up to this “Advanced” threshold, including:
- Medicare Shared Savings Program ACOs, Tracks 2 and 3;
- Medicare Next Generation ACOs;
- Comprehensive Primary Care Plus (CPC+) Model;
- Oncology Care Model (two-sided risk); and
- Comprehensive End-Stage Renal Disease Care Model (Large Dialysis Organization arrangement).
Notably absent from this list of proposed approved Advanced APMs are Track 1 MSSP ACOs and various bundled payment models.
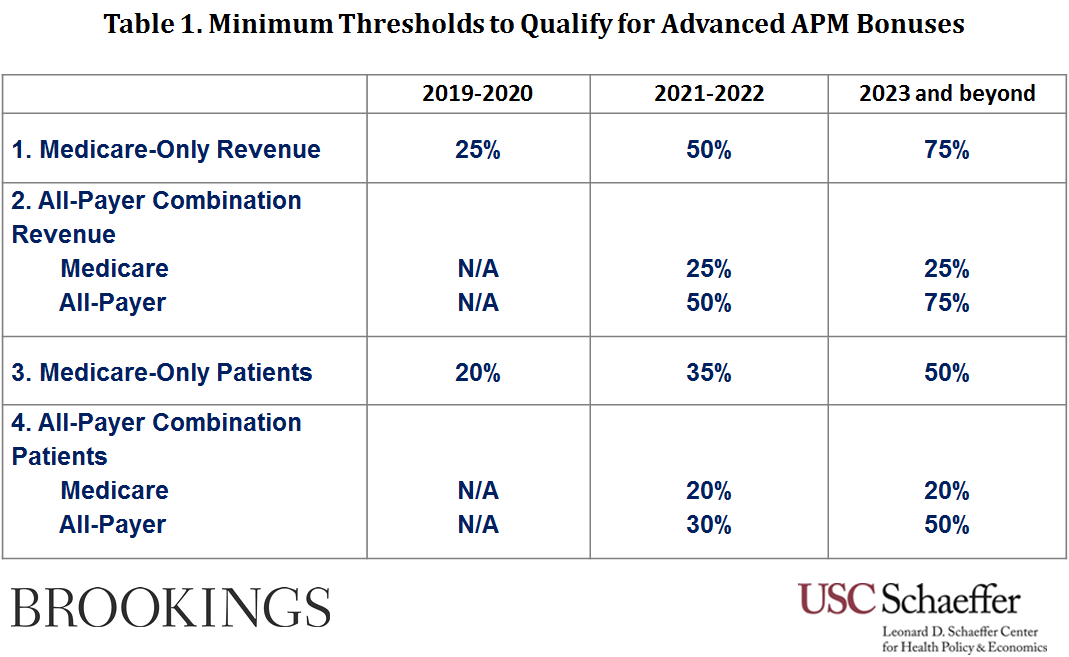
By earning a sufficient percentage of their revenue through an Advanced APM, physicians can qualify for a bonus payment equal to 5 percent of their annual fee-for-service revenue in years 2019-2024 and a 0.5 percentage-point higher annual fee rate increase than physicians and other providers in MIPS each year starting in 2026 (0.75 percent vs. 0.25 percent). Alternatively, as a new feature under this rule, physicians can also qualify by seeing a sufficient percentage of their patients through an Advanced APM; notably, the patient percentage thresholds are lower than the revenue percentage thresholds.
Specifically, for physicians participating in Advanced APMs, there are four ways to qualify for the bonuses and higher payment updates of the Advanced APM track. Across all, the thresholds increase in the initial years and remain constant from 2023 onward. However, the thresholds are distinct in whether they are based on revenue or patient volume, as well as whether they are based on Medicare alone or on all payers. The four categories for qualification are:
1. Earn a minimum percentage of their Medicare Part B revenue through an Advanced APM;
2. Starting in 2021, earn a lower minimum percentage of their Medicare Part B revenue AND a minimum percentage of their revenue from all payers through an Advanced APM;
3. See a minimum percentage of their Medicare patients through an Advanced APM; or
4. Starting in 2021, see a lower minimum percentage of their Medicare patients AND a minimum percentage of their patients from all payers through an Advanced APM.
Importantly, if physicians and other providers fall short of these minimums, they would not qualify under the Advanced APM track. However, physicians and other providers participating in APMs who meet the lower “Partial Qualifying Provider” percentage thresholds for either revenue or patients can choose to opt out of MIPS reporting altogether, guaranteeing that they will receive neither a penalty nor bonus for the year. Further, the providers participating in APMs that were not designated Advanced may still qualify as MIPS APMs and receive some automatic credit under the Clinical Practice Improvement Activities (CPIA) category.
Potential for low specialist participation in the Advanced APM program
Over time, MACRA is likely to continue to evolve and the All-Payer Combination Advanced APM option will become available, making payment models developed by private insurers increasingly available and allowing more payment models to gain “advanced” recognition.
Notably, however, the “advanced” list does not include any of the current bundled payment models established by CMMI. This omission will be particularly critical to specialists, as bundled payments represent a significant share of their participation in APMs and many of the proposed “advanced” APM qualifiers have more effectively engaged primary care physicians and other providers than specialists to-date.
To this end, in their proposed rule, CMS’ requested comment on how to offer an option based on bundled payments, a model that has garnered comparatively greater specialist participation. Bundled payments as a concept have often been cited by economists and health care policymakers as a strong policy lever to shift to value-based payment, but their exclusion may effectively limit many physicians and other providers.
Concluding thoughts and outstanding questions
With only six months before physicians’ performance will have an impact on their payment under MACRA, physicians are intensely scrutinizing the two payment incentive programs and how they would fare under them. But most are confused about how best to navigate the various programs given the complexity of the rules and options. The lack of timely data with which to assess their performance on an ongoing basis may further handicap the ability of physicians to make informed choices and improve their performance.
While the proposed rule elucidates many elements of the new payment systems and the final rule will help clarify some remaining questions, many questions about moving parts remain, including those related to: the different risks and rewards for MIPS vs APMs; the uncertainty of movement between both pathways; and the potential for additional payment models (such as the Physician-Focused Payment Model option). These and other uncertainties have raised concerns about the viability of small practices in this environment and the risk that MACRA will lead large numbers of physicians to seek employment by hospitals and large physician organizations. This risks potentially leading to to much higher degrees of consolidation and losses in physician productivity.
MACRA remains a fundamentally important change from the status quo. It offers significant promise to change—and hopefully improve—physician practice and move payment from volume to value. Without question, its implementation will be watched intently.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).