Created within a year of each other, the World Bank and the United Nations were born out of a shared response to the Second World War. The war created a constituency willing to invest resources and ideals in a system of multilateral cooperation. In the words of one of their architects, these institutions were to create a “New Deal for a new world.”
Today we face another period of global disorder. The number of armed conflicts worldwide has tripled from four to 11 since 2007. 2014 was the most lethal year since the end of the Cold War, according to the Uppsala Conflict Data Program. In the same year, the total number of deaths from terrorism increased by 80 percent, to close to 37,000, the largest yearly increase in the last 15 years, according to the Institute for Economics and Peace.
The fallout is clear. The number of people affected by humanitarian crises has almost doubled in the past decade, with 125 million people requiring humanitarian assistance. Displacement is at a post-World War II high with 60 million people around the world forced from their homes, often within their own countries. Roughly two-thirds of U.N. peacekeepers today and almost 90 percent of personnel in U.N. Special Political Missions are working in and on countries where there is little peace to keep.
Responding to this challenge, the U.N. and its member states led major reviews in 2015 of the tools and approaches used to respond to conflict. These reviews looked at peacekeeping operations, the implementation of Security Council Resolution 1325 on Women, Peace, and Security, and the U.N.’s peacebuilding architecture.
These reviews underscored that while humanitarian assistance can mitigate suffering, and peacekeepers can stabilize situations, they alone cannot create lasting peace, development, and prosperity.
Responding to this challenge requires a new global partnership to prevent violent conflict, reduce humanitarian need, and sustain peace. This partnership must reaffirm our commitment to humanity and chart a course for change, as the secretary-general has called for in his recent report for the World Humanitarian Summit.
Taking place just before the World Humanitarian Summit, the ministerial meeting of the International Dialogue on Peacebuilding and Statebuilding (IDPS) in Stockholm is a key moment at which the principles of the New Deal for Engagement in Fragile States, in particular the TRUST and FOCUS components, could be used to provide a foundation for this effort.
Peacebuilding and statebuilding, however, are political. Technical instruments must be aligned with and informed by a political strategy owned by national governments and developed in consultation with its people. This is as true at the global level as it is in each country.
What needs to happen?
The first step is normative. In 2015, through the Addis Ababa Action Agenda and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, member states committed to a future that aims to leave no one behind. The International Dialogue, the New Deal, and the g7+ were important foundations, asserting the links between development and peace captured in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). However, the SDGs are universal. Goal 16 on just, peaceful, and inclusive societies is an ambition of all countries, not only those identified internationally as conflict-affected, and other goals—for example SDG 1 on ending poverty and SDG 10 on reducing inequality—are critical to peace in conflict-affected states. A statement at Stockholm should be made clarifying the linkages between the specific focus of the New Deal and the universal goals of the SDGs (and their affiliated processes).
The second is ownership. Peace and development are first and foremost a national responsibility. The New Deal provides a framework that brings together multilateral and bilateral partners of conflict-affected countries. However, it has functioned primarily as a tool for the targeting of aid, not its management. To achieve the SDGs in 2030 we need to equip national partners with the tools to address the drivers of conflict. That is where a revitalized New Deal can play an important role. While the SDGs are now the overarching framework, making more significant progress on the TRUST and FOCUS components of the New Deal will be essential contributions to the implementation of the 2030 Agenda. Commitments to ownership, the use of country systems, and mobilization of national resources should be restated and given life in Stockholm.
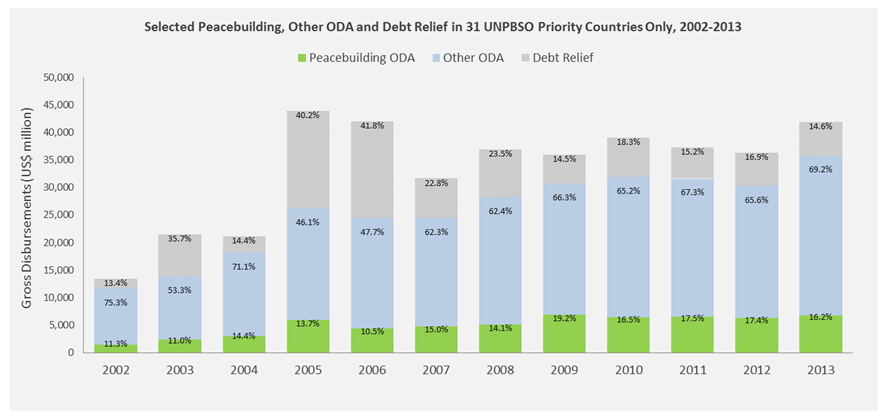
The last is resources. Resolving conflict requires multi-year financing addressing the drivers of conflict rather than short-term responses. While official development assistance (ODA) to conflict-affected countries has increased over the last dozen years or so, in 2013, peacebuilding support to legitimate politics, security, and justice systems represented only 16 percent (or $6.8 billion) of the $42 billion in gross development assistance for 31 conflict-affected countries (see Figure 1). At a very moment of global crisis, as of January 1, 2016 and for the first time in its history, the United Nations Peacebuilding Fund will not reach its $100 million annual allocation target endorsed by the secretary-general and donors. Stockholm needs to demonstrate a commitment to peacebuilding and statebuilding that goes beyond words, and commit to more resources devoted to conflict-affected countries and more resources targeting the drivers of conflict.
Figure 1: Peacebuilding versus total ODA, debt relief included, 31 conflict-affected countries, 2002-2013
The U.N. has been a supporter of the New Deal from the beginning, recognizing it as a model for partnership between conflict-affected states and their development partners. A political, prioritized strategy for peacebuilding and statebuilding is necessary to support full implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals in conflict-affected states. The New Deal provides inspiration for such a strategy. The question for Stockholm is whether inspiration alone will be sufficient.
Note: Special thanks goes to Jago Salmon for his contributions. This blog reflects the views of the author only and does not reflect the views of the Africa Growth Initiative. Similarly, the views expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the United Nations.

Commentary
A new deal or a new global partnership for conflict-affected states?
March 30, 2016