What makes the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) consequential?
Since the onset of the 21st century, countries from every corner of the world have vigorously negotiated free trade agreements (FTAs) based on the principle of preferential market access (as opposed to the most-favored nation obligation of the WTO). This has resulted in a veritable avalanche of such trade deals, with close to 400 FTAs notified to the WTO in the past 20 years. If the negotiation of preferential trade agreements is now the dominant trend in the trading regime, and almost no country has escaped contagion from the FTA syndrome, why does one agreement in particular—the TPP—remain the focal point of policy debates on trade?
Chart 1. Multilateral trade regimes and FTA proliferation
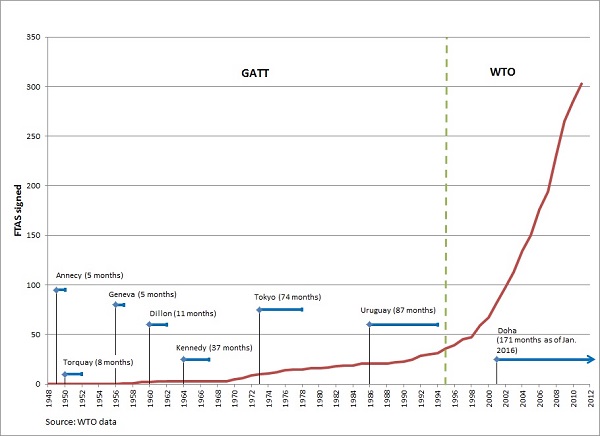
The TPP generates most attention because it has spurred the emergence of mega trade agreements (as compared to the mostly small bilateral trade deals that had characterized the FTA wave), and has offered a new platform to advance the trade agenda as negotiations on the Doha Round continue gridlocked. The TPP has come a long way from its humble beginnings as a trade grouping of four small open economies (Brunei, New Zealand, Chile, and Singapore). Today, it comprises 12 nations, covers 26 percent of world trade, and is expected to generate global income gains in the neighborhood of $492 billion by 2030.
Chart 2. From humble beginnings to mega trade deal
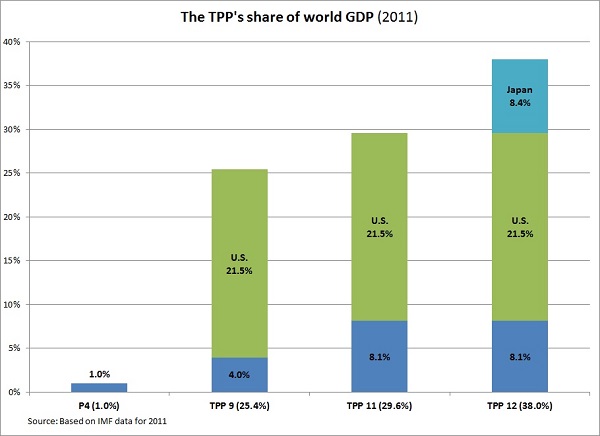
But the significance of the TPP is not to be grasped by numbers alone. Consider the following defining traits of this trade agreement:
- Its high level of ambition for tariff liberalization vowing to disallow sectoral carve-outs. While it is true that sensitive sectors asserted their political weight by deferring or limiting tariff elimination (e.g., autos for the United States and five agricultural commodities for Japan), the commitment of TPP countries to eventually eliminate 99-100 percent of tariff rates is indeed impressive. Japan does stand out for a lower level of committed tariff elimination (95 percent); but again this is the highest level of liberalization that Japan has ever committed to in any trade negotiation.
- Its comprehensive set of rules to target non-tariff barriers by introducing disciplines on issues such as regulatory coherence, state-owned enterprises, competitiveness, supply chains, etc. With 30 chapters and over 5,000 pages of text, grasping the reach of TPP rules will certainly take time. However, a quick glance does reveal novel, and needed, disciplines in important areas of the economy. For example, the e-commerce chapter establishes a binding obligation for governments to allow free data flows, disallows forced localization of data servers (except for the financial sector), and mandates that all countries must provide a legal framework to protect personal information. Another important innovation is the TPP provision that governments cannot require the transfer of source code from private companies operating in their market.
- Its expansive vision as an Asia-Pacific platform with aspirations to set global standards. Its open architecture with a docking mechanism to encourage further member expansion and its explicit aim to establish a trans-regional platform that bridges Asia and North and South America are strong selling points for the TPP. It undercuts the oft-mentioned fear of using preferential trade agreements to create closed-off regions, and it gives its rules and standards the opportunity to disseminate far and wide.
- Last but not least, the TPP has emerged as a central policy priority for both the U.S. and Japan to hone their international economic competitiveness and achieve broader foreign policy goals. In the area of foreign economic policy, the TPP is one of the most compelling frameworks to encourage China to deepen its market reforms and sign on to more ambitious liberalization commitments. The TPP, therefore, has emerged as a central arena for the interaction of the three giants of the world economy.
The TPP’s effect for the United States and Japan
The United States as a Pacific power
The U.S. expects to reap important economic benefits from the TPP. It is a trade agreement that taps into the areas of competitive strength of the American economy: agricultural exports, trade in services, the digital economy, to name a few. Econometric studies put the expected income gains of the TPP for the U.S. in the order of $131 billion per year, and to the extent that the TPP becomes a global standard, these gains will grow. Indeed, the TPP is the centerpiece of the American trade agenda. Its success is required for continued momentum in the on-going trans-Atlantic trade negotiations, but it could also influence other important trade initiatives. For example, TPP disciplines on services and state-owned enterprises are expected to influence deliberations on the Trade in Services Agreement, a plurilateral trade negotiation carried out under the aegis of the WTO.
From the point of view of global governance, the TPP is a litmus test of the U.S. ability to provide leadership at a time of great complexity in the world economic order: one where supply chains have emerged as a main driver of production and trade, where emerging economies are increasingly vocal in the management of the global economy, and where the test of updating Bretton Woods institutions looms large. Through the TPP, the U.S. can display its convening power to negotiate novel trade rules, to devise new institutional forms that complement and spur on the multilateral regime, and to be proactive and not just reactive to initiatives from rising economic powers.
But the TPP is also a pillar of U.S. Asia policy, one that solidifies the U.S. commitment to remain an engaged Pacific power. This trade agreement increases the appeal of the rebalancing policy by defining it not just as a reorientation of military resources toward a region undergoing a significant power transition; but also as the pursuit of a common endeavor: furthering economic interdependence with rules that match the realities of the 21st century economy, and potentially establishing a bridge toward China with the prospect of TPP membership.
Japan is an essential partner for the U.S. to achieve these important goals. Japan came late to the TPP negotiations (in the summer of 2013), but it transformed the economic and political significance of this deal. Japan’s participation allowed the TPP to qualify as a mega trade agreement. For the U.S. alone, the projected economic gains with Japan on board tripled. This is not surprising given the size of the Japanese market and the fact that the U.S. and Japan do not have a bilateral trade agreement; nor has Japan ever accepted these levels of liberalization. Moreover, prior to Japan joining the TPP there were doubts as to whether this could indeed become an Asia-Pacific platform of economic integration since no major Asian economy was participating. Japan’s entry put those objections to rest.
Japan as a reviving power
For Japan as well, the TPP negotiations have had salutary effects on its trade diplomacy and on the pursuit of central domestic and foreign policy priorities. Prior to joining the TPP, Japan’s trade strategy had achieved modest results: it lagged behind its peer competitors in negotiating an FTA network that covered a substantial share of its trade, it had faced difficulty in persuading Southeast Asian countries to adopt many WTO+ rules, it had received the cold shoulder from the U.S. and Europe as it proposed the negotiation of trade agreements, and remained deadlocked with China over the membership configuration of an East Asian trade grouping. The TPP altered the parameters of Japanese trade policy. It allowed the country to negotiate preferential access to main markets of destination, to disseminate next frontier trade rules, and to undertake concurrent mega trade negotiations. As a reaction to Japan’s courting of TPP membership, China recalibrated its trade policy to speed up the launch of trilateral trade negotiations in Northeast Asia and was now amenable to a 16-member trade grouping upholding the principle of ASEAN centrality (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership or RCEP), and the Europeans also came to the negotiation table.
As a full participant in the mega FTA movement, Japan can aim high in order to pursue signature objectives such as:
- Negotiate deep integration FTAs that enhance the international competitiveness of Japanese global supply chains. An assessment of Japan’s core competencies in the 21st century should start with the recognition that a significant share of industrial capacity has been relocated overseas. On-shoring of manufacturing operations is not a viable goal given projected demographic trends. Rather, the aim should be to sustain and strengthen Japan’s role in global supply chains (the leading force of international production and trade today). Japan’s international diplomacy has a role to play here by negotiating deep FTAs that meet the needs of fragmented production chains. Additionally, deep FTA commitments will also help Japan address its own domestic inefficiencies such as the modest liberalization of the services sector.
- Lock-in structural reforms. One of the main benefits of linking the domestic structural reform agenda to international trade commitments is that it will be harder to roll back the reforms if and when political circumstances change (this is indeed a major lesson of the failure to institutionalize Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi’s reforms). Importantly, the TPP negotiations do not conform to the old-style gaiatsu pattern where a reluctant Japan would deflect U.S. pressure for it to change its ways. This time Japan has eagerly sought to be at the TPP table and has—of its own accord—identified the synergies between the new trade commitments and its own efforts to reform the domestic economy.
- Manage the transition from “regime-taker” to “regime-maker.” With the stagnation of the WTO, we have moved to a system of decentralized competition whereby different clusters of countries seek to define the standards for economic integration. The costs of a passive trade policy are much higher today than in a most favored nation (MFN) world where preferential trade agreements were the exception and not the rule. The expectation of steady liberalization benefits through successive multilateral trade rounds has been sharply revised. Therefore, countries that want to avoid the discriminatory effects of existing preferential trade deals and to improve access to important markets through additional elimination of tariffs and the adoption of rules that address behind-the-border barriers have resorted to an active FTA diplomacy. More broadly, Japan has much to win from displaying leadership in international economic governance, in a manner that resonates with the goals of the Abe administration to play a proactive role in world affairs.
Conclusion of TPP talks: Significance and impact
For all the shared interests between the U.S. and Japan in the TPP project, negotiations over long divisive market access terms proved difficult and frustratingly long. Of course, a host of other issues also kept the larger TPP membership apart. Biologics especially was the last topic to close in the final TPP ministerial held in Atlanta in October 2015, and negotiations went to the wire. Despite all these difficulties, the ability to strike a TPP deal last fall represents a big win for the trade regime which has not seen a success of this magnitude in two decades. Since its creation, the WTO has not updated the rules of international trade and investment, and the Doha Round lingers on life support. Many were skeptical that a major trade negotiation tackling front and center the complex and unwieldy behind-the-border agenda could succeed. This is the most powerful message coming from Atlanta: it can be done.
With a TPP deal in hand there is greater hope that we can manage the tectonic changes in international trade governance. The transformation of the trade agenda (increasingly about regulatory matters) and the limitations of the WTO as a negotiation forum, have called into question the pure multilateral ideal—one set of binding rules for 150+ countries. Instead, the center of action is now on what we call “variable geometry” arrangements where subsets of countries negotiate next-frontier rules: the plurilaterals in the WTO and the preferentials through mega trade agreements. The emerging system for trade governance is not risk-free, and much effort will be required to forestall potential dangers: fragmentation (if TPP-like standards do not disseminate widely) and exclusion (if less developed countries are bypassed by the FTA wave).
Moreover, the TPP deal opens a new and promising chapter in U.S.-Japan relations. It is certainly more than a U.S.-Japan trade agreement—it represents the ability of 12 countries at varying levels of development and with very different regulatory regimes to agree on the most substantive trade liberalization to date. But it is also true that at the core of the TPP, the U.S. and Japan as the largest and most developed economies have acted as an engine of negotiations. The TPP marks a milestone in U.S.-Japan relations, as an effective instance of cooperation to upgrade the international economic architecture. In the TPP, the U.S. and Japan are on close alignment on the rules area of the talks and were able to reach an agreement on market access issues that in the past had proven intractable.
Ratification, reform, and reach
None of these effects will be long lasting nor will they reach their full potential, if TPP countries (and the U.S. and Japan in particular) do not double down on the next crucial steps. For simplicity sake, these can be dubbed the three “Rs” of ratification, reform, and reach.
Ratification
Ratification rules in the TPP require that six countries representing 85 percent of combined GDP approve the agreement before it enters into force. Therefore, to meet this numerical requirement both the U.S. and Japan must ratify. However, for the U.S., TPP ratification will represent a steep political battle in the midst of an American presidential election year. Despite public opinion polls showing that most Americans see in international trade an opportunity, the politics of trade agreements are fractious. Long-standing opposition by environmental groups and unions to trade agreements has resulted in their active mobilization against the TPP. And the debate on the merits of trade agreements has only become more heated as critics suggest that trade globalization is to be blamed for growing income inequality and the erosion of state regulatory powers.
For both national parties, the TPP is a divisive issue. While President Barack Obama has made TPP negotiation and ratification a central priority of his administration, Democrats in Congress have not backed his trade initiative in large numbers, in part due to the opposition of the party’s traditional base, labor unions. The internal dynamics of the Republican Party have shifted dramatically, complicating the odds for the TPP. The Republican Party has become less cohesive with the emergence of the Tea Party wing determined to deny Obama a legacy-making trade agreement. The support of key Republican figures in the Senate has also waned due to dissatisfaction over the tobacco carve-out from investor-state dispute settlement and the exclusivity period for biologics. And the business community has also criticized these provisions, offering only qualified support for the TPP deal.
The U.S. has yet to fail in ratifying a negotiated trade agreement. And a vote down on the TPP would be singularly costly for the credibility of U.S. foreign policy and the evolution of the international trade regime.
Reform
One of the most powerful benefits of trade agreements is the ability of governments to use them as commitment devices to implement needed economic changes. Reform is in fact the crucial issue for Japan as it tries to leave behind stagnant growth. Economic revitalization certainly goes beyond agricultural reform, to encompass the host of productivity-enhancing measures across all areas of the economy, the internationalization of services, the promotion of inward direct investment, and the further upgrading of regional and trans-regional production networks.
Yet, farming countermeasures adopted in the wake of the TPP deal have raised doubts about the government’s resolve to transform its agricultural sector. Japan’s TPP market access commitments do include a 56,000-ton import rice quota (to grow eventually to 78,400 tons). But the government promptly announced an increase in stockpiling purchases to match the TPP quota, effectively preventing a drop in the price of rice and market adjustment. This artificial support preempts the modernization of the agricultural sector since it enables part-time farmers to continue operating in tiny plots, hindering the emergence of commercial farming. The government also submitted a generous 2016 supplementary budget with 312 billion yen earmarked for agricultural TPP countermeasures. But informed experts question its impact in boosting farming competitiveness since public works allocations still loom large (30 percent of outlays will go to land reclamation projects).
Just as the electoral cycle has not facilitated TPP ratification in the U.S., the looming Japanese Upper House election in July is not conducive to moving past prior trade compensation practices.
Reach
The release of the TPP text has clarified a very important point: membership can be extended not only to APEC economies but also to other countries that are willing to meet TPP disciplines. Enlargement will be critical to avoid the above-mentioned risks of fragmentation and exclusion by helping disseminate TPP standards. In the short and medium term, the conclusion of the TPP talks is expected to have two main effects: increase the list of potential applicants, and encourage a higher level of ambition among on-going trade negotiations.
The number of economies expressing an interest in joining the TPP has grown to include South Korea, Taiwan, Indonesia, Thailand, the Philippines, Colombia, and Costa Rica, among others. Regarding the second wave of accession the key issue will be readiness to undertake the ambitious liberalization commitments of the TPP, and the list of prospective applicants shows wide variation on this score. The conclusion of TPP talks also creates an incentive for the updating of existing FTAs and/or scaling up the level of ambition in ongoing trade negotiations, as countries outside the TPP want to secure export markets, attract foreign direct investment, and embed their companies in global supply chains.
In the long run, the key challenge will be to devise an effective strategy to engage emerging economies, such as China, India, and Brazil. This is still the gaping hole in the U.S. plans to develop trans-Pacific and trans-Atlantic trade groupings. Certainly, putting in place the TPP and the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership is the first step in such strategy since it changes the incentive structure for these countries to entertain further market liberalization. But at the end of the day, these emerging economies must reach the determination that it is in their national interest to abide by these economic standards, and find the political will to tackle vested interests. This is a tall order indeed.
The most pressing question may well be how China will position itself vis-à-vis the TPP. Can we expect it to act on past precedent and seek TPP accession just as in the past it used WTO membership to advance economic reforms? Or will it choose instead to champion the negotiation of a Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP) after both the TPP and RCEP materialize, in order to play a more proactive role in the international economic architecture—more in conformance with the recent launch of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank?
The recently struck TPP agreement underscores the potential of furthering U.S.-Japan cooperation to supply needed international economic governance. However, the overview of remaining challenges also shows that clinching a TPP deal is just the first step.
This article originally appeared in the March/April 2016 issue of
Economy, Culture & History Japan SPOTLIGHT Bimonthly
.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).



Commentary
The high stakes of TPP ratification: Implications for Asia-Pacific and beyond
March 10, 2016