The Middle East never lacks for commentary and opinions. But what do scholarly experts on the Middle East think? In a piece originally published by the Washington Post’s Monkey Cage blog, Marc Lynch and Shibley Telhami discuss new survey data.
Is the Israeli-Palestinian two-state solution dead? Would a Biden administration decision to return to the JCPOA — the 2015 Iran nuclear deal — reduce the risk of Iran obtaining a nuclear bomb? How important were the Arab uprisings a decade ago, and are they coming back?
The Middle East never lacks for commentary and opinions. Several high-quality surveys regularly ask political scientists and foreign policy experts their views on U.S. policy in the region. But what do scholarly experts on the Middle East think?
Last week, we fielded a unique survey of scholars with expertise in the Middle East, the first of our new Middle East Scholar Barometer. Drawing on the membership of the Middle East Studies Association, the American Political Science Association’s MENA Politics Section and the Project on Middle East Political Science at George Washington University, we identified 1,293 such scholars. The vast majority speak regional languages, have spent significant time in the Middle East, and have dedicated their professional lives to the rigorous study of the region and its politics. Within three days, 521 scholars had consented and responded (a 40% response rate), divided almost equally between political scientists and nonpolitical scientists.
We asked these experts descriptive questions, not what they thought should happen — or would probably happen — in the Middle East. The survey asks for their assessment of the region as it currently exists and might exist a decade hence. It did not ask about their preferences on outcomes or policies.
The results of the survey paint a fascinating picture of the Middle East, and valuable insights that the Biden administration — which has said it aims to take the views of experts seriously — might consider as it crafts U.S. foreign policy for the region.
Israel and the Palestinians: A one-state reality akin to apartheid
Perhaps the starkest finding of the survey is the collective assessment of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. A strong majority, 59%, describes the current reality for Israel and the Palestinians as “a one-state reality akin to apartheid.” An additional 7% view it as a “one-state reality with inequality, but not akin to apartheid.” Only 2% describe the situation as a temporary Israeli occupation of the West Bank and Gaza; 30% describe the current situation as semi-permanent occupation by Israel.
While the Biden administration will probably seek to kick-start diplomacy, the experts offer little hope for achieving a two-state solution. In our survey, 52% say that such an outcome is no longer possible, while 42% find it unlikely within the next 10 years. Only 6% consider it probable within the next decade.
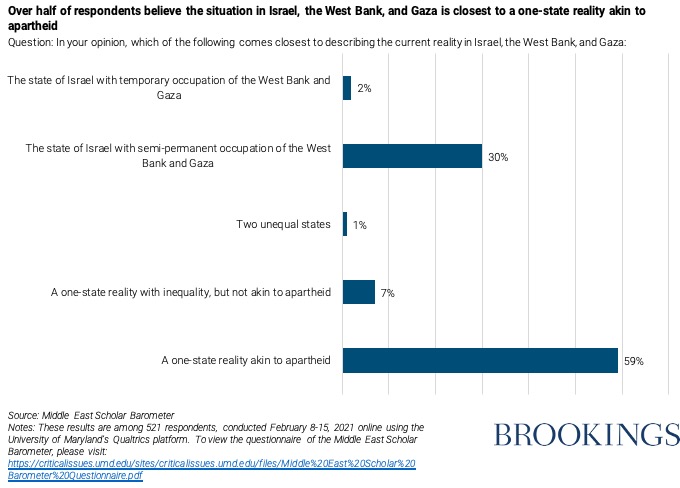
Those expectations are especially bleak because without a prospect of a separate Israel and separate Palestine, 77% expect to see a one-state reality akin to apartheid, while another 17% expect a one-state reality with increasing inequality, but not akin to apartheid. Only 1% expect to see a single binational state with equal rights for all.
Iran and the nuclear deal
The United States returning to the Iran nuclear agreement (the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, or JCPOA) as it’s currently written would make it less likely that Iran would get a nuclear weapon within the next decade — that’s what 75% of our survey respondents say. And 21% say returning to the JCPOA would make no real difference — only 2% say a return would make an Iranian nuclear weapon more likely.
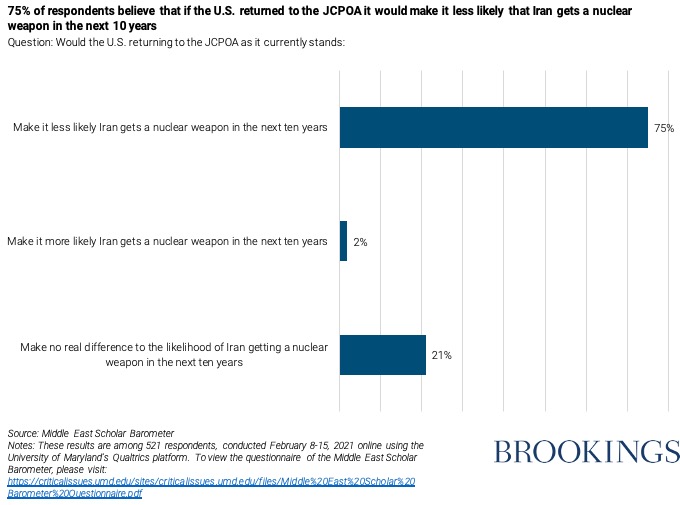
Perhaps unsurprisingly, the scholars overwhelmingly oppose either military action against Iran or a continuation of the Trump administration’s “maximum pressure” policy. The primary divide was over tactics: Sixty-seven percent say the U.S. immediately returning to the JCPOA before addressing other issues would better serve U.S. interests, while 23% prefer first negotiating a grand bargain including ballistic missiles and regional policies in alignment with allies such as Israel, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates.
What happened to the Arab Spring?
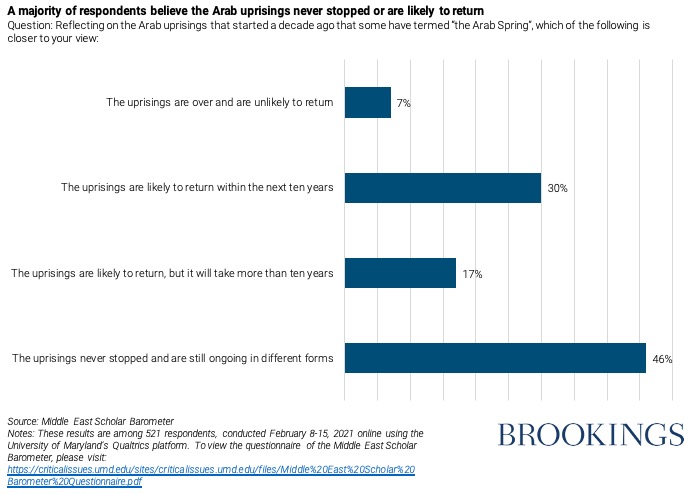
The experts in our survey tended to disagree over the future and the significance of the 2011 uprisings that rocked the Arab world. A majority of scholars say that the uprisings remain active: Thirty percent expect another wave of mass protests within the next decade, while 46% say that the uprisings are still ongoing in different forms. Only 7% think that the uprisings are over and gone, while 17% think they probably won’t recur for at least a decade.
But did they matter? A slim majority, 54%, describe their impact as significant, but not transformational. For 29%, the uprisings were transformational, while 17% view them as a temporary disruption with little long-term impact.
And what about the U.S. and the Middle East?
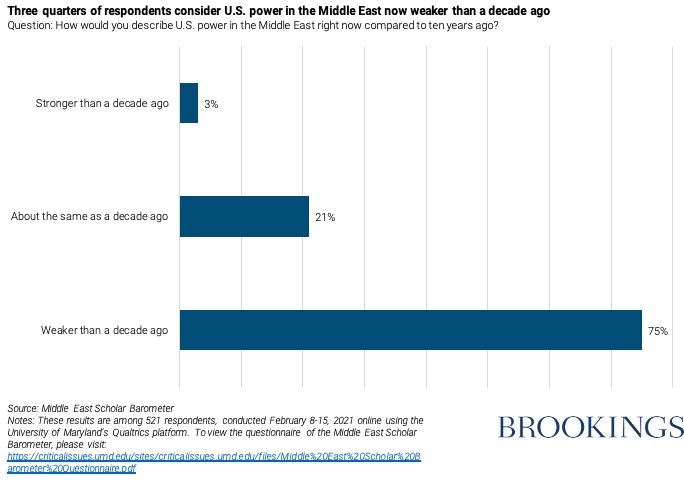
Only 3% of the scholars view the United States as stronger in the Middle East today compared with a decade ago, while 75% view the United States as weaker. Quite strikingly, only 38% still view the United States as the single dominant external power in the region. This is not primarily about Russian competition — only 8% see a Cold War-style bipolar region. A slight majority (54%) view the region as multipolar, with a number of great powers competing for influence and power. For those who believe in enduring U.S. primacy, these results should open eyes.
Nor do the scholars see a coming revival of U.S. primacy. Looking ahead, only 10% expect the United States to be stronger a decade from now. This doesn’t necessarily mean precipitous decline: Forty-eight percent expect the United States to be weaker in a decade, while 41% expect it to be about the same as it is now. Intriguingly, scholars do not agree on whether there has been a general decline in the importance of external countries in what happens in the Middle East: Forty-two percent say external powers have about the same amount of influence as a decade ago, 29% say they have more influence, and 28% say they have less influence.
What’s ahead for the Middle East — and the United States? The Biden administration has signaled it would listen to experts, to avoid disasters such as the 2003 Iraq War. This unique survey could help new U.S. policymakers understand the realities of the Middle East as scholars of the region see them.
-
Acknowledgements and disclosures
Rachel Slattery performed graphic design for this piece.







Commentary
Biden says he will listen to experts. Here is what scholars of the Middle East think.
February 19, 2021