When California passed its 2016 budget late last month, it joined a growing list of states that have recently adopted or expanded state versions of the federal Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). First enacted in 1975, the EITC has become one of the country’s most effective antipoverty programs. We estimate that the federal EITC keeps millions of individuals and children out of poverty each year, reducing the national poverty rate by several percentage points. Others have shown how the EITC creates a strong incentive to work and works as a powerful tool for reducing income inequality.
How the federal EITC works
For an unmarried worker with one child in 2015, the federal EITC works like this: Up to her first $9,880 earned, the worker receives a tax credit equal to 34 cents on the dollar, for a maximum credit value of $3,359. The credit is reduced by 16 cents for each dollar earned beginning at $18,110, eventually phasing out at $39,100 in earnings. Phase-in and phase-out rates and ranges depend on a worker’s filing status and number of dependents claimed. Importantly, the EITC is refundable; a filer can still claim any credit in excess of her tax liability, contributing to refunds that can represent double-digit shares of annual income for lower-paid workers.
Most states have their own EITCs
Of the 26 states and the District of Columbia with their own EITCs, most have structured their programs to mirror the federal EITC, by simply matching some percentage of the federal credit in a given tax year (see map). This year, Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Rhode Island all increased their state EITCs’ matching percentages. In three states, the EITC is non-refundable, making it a less effective incentive for very low-income workers (Maine this year made its credit refundable). California’s EITC joins a couple of others that, while still refundable, vary in the degree to which they mirror the federal credit based on filing status and income.
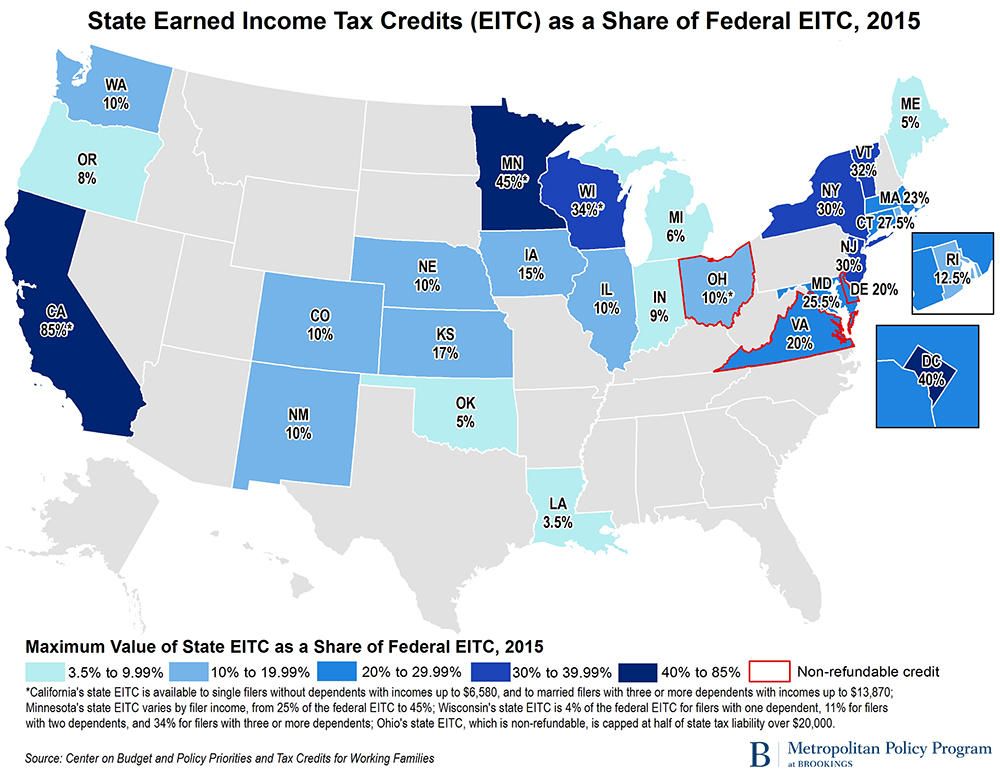
State EITCs: Not perfect but increasingly important
Through our work maintaining Brookings’ EITC Interactive, we hear regularly from stakeholders around the country engaged in efforts to expand the EITC and increase local participation to strengthen low-income families and communities. Although it is difficult to determine uptake rates locally, there are several factors associated with participation. Self-employed workers are less likely to claim the credit, as are workers with low English proficiency, and those who do not claim any dependents. The availability of tax preparation assistance tends to increase participation rates. For groups who hope to expand access to the EITC in their communities, these considerations are a good place to start.
To be sure, the EITC is not a silver bullet. Because it is explicitly tied to work effort, the credit does not support low-income families who can’t find work. And because states must balance their budgets, many have had difficulty sustaining their EITCs during periods of economic downturn. (Several of the recent state EITC expansions actually represent the restoration of benefits following drastic cuts during the Great Recession.) Additionally, the federal EITC and its state analogues provide only modest support to workers who do not claim any dependents on their tax return. As such, policy makers should consider state EITCs strong complements to other interventions, such as the growing number of increases in the minimum wage occurring in states and cities.
Nevertheless, the EITC remains one of the best tools we have to fight poverty. Despite bipartisan support for the federal EITC, it is unlikely to be expanded anytime soon. In that light, recent state EITC expansions may be helping to create a more responsive, sub-national safety net that better reflects a large and diverse nation where local priorities and needs differ markedly.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).



Commentary
States adopt and adapt the EITC to address local need
July 29, 2015