April 15 is tax day, but not many Americans will be lining up at the post office or logging onto TurboTax as midnight approaches. Taxpayers who receive refunds often file well ahead of the April 15 deadline. And according to new research, many of those refund dollars are already spent or spoken for.
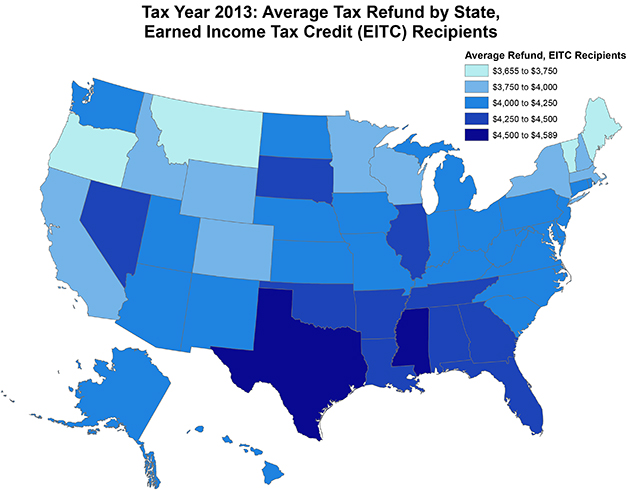
Early filing is particularly common among taxpayers who claim the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), which supplements earnings for low-income workers and their families. EITC recipients often receive substantial refunds, especially in relation to their income. According to new data available through our EITC Interactive, nationwide 26.8 million taxpayers benefited from the EITC for the 2013 tax year, and they claimed a total of $64.7 billion from the credit. Combined with other credits and over-withholding these families received, the average refund for EITC filers topped $4,100 that year. As the accompanying map shows, that amount approached $4,500 or more in many southern states.
I thought of those large refunds while reading a fascinating new book by sociologist Kathryn Edin and her colleagues, titled, It’s Not Like I’m Poor: How Working Families Make Ends Meet in a Post-Welfare World. The book provides insights from in-depth interviews with 115 families with children in the Boston area who claimed the EITC. It examines their household budgets and how the families view and use the credit. The authors find that these families rely greatly on their tax refunds to close the gap between the wages they earn and the daily costs of living in an expensive region like Greater Boston. For some, a large tax refund also enabled them to purchase something normally confined to middle-class families, such as a special birthday present for a child or dinner out at a restaurant.
One of the authors’ central findings, however, was that EITC recipients bear a considerable amount of debt—95 percent of the families studied had debt of some kind. The most common (66%) was credit card debt, with the typical family owing nearly $2,000. Considerable shares of families also had utility, car, or student loan debt.
Their indebtedness was not surprising given that wages covered on average only about two-thirds of monthly expenditures. The authors classified one-quarter of families’ refund spending as dedicated to debt/bills, but other ways families spend the money—such as repairing a car or paying ahead on bills—point to the lack of financial cushion EITC recipients endure throughout the year.
For the families Edin and colleagues studied, the average tax refund represented a staggering three months of earnings. Despite that, the authors report that many families expressed that they preferred the “windfall” versus receipt of payments over several months, partly because the lump sum held out the prospect of helping them save. But one has to wonder if the EITC, now routinely referred to as the nation’s most effective anti-poverty policy, best supports families’ financial security in this form, as its recipients fall further behind each month.
We should experiment with new ways of delivering EITC recipients’ tax refunds that preserve some of its windfall aspect while also periodically delivering portions of the credit throughout the year. A small periodic payment pilot is underway in Chicago, and early findings suggest that advance payments of taxpayers’ anticipated EITC helped them meet basic needs, pay off debt, and reduce financial stress relative to similar families not receiving such payments. It’s time to try making the EITC more than an annual boom in a bust-filled financial cycle for low-income families.


Commentary
Time to create multiple tax (refund) days for low-income filers
April 14, 2015