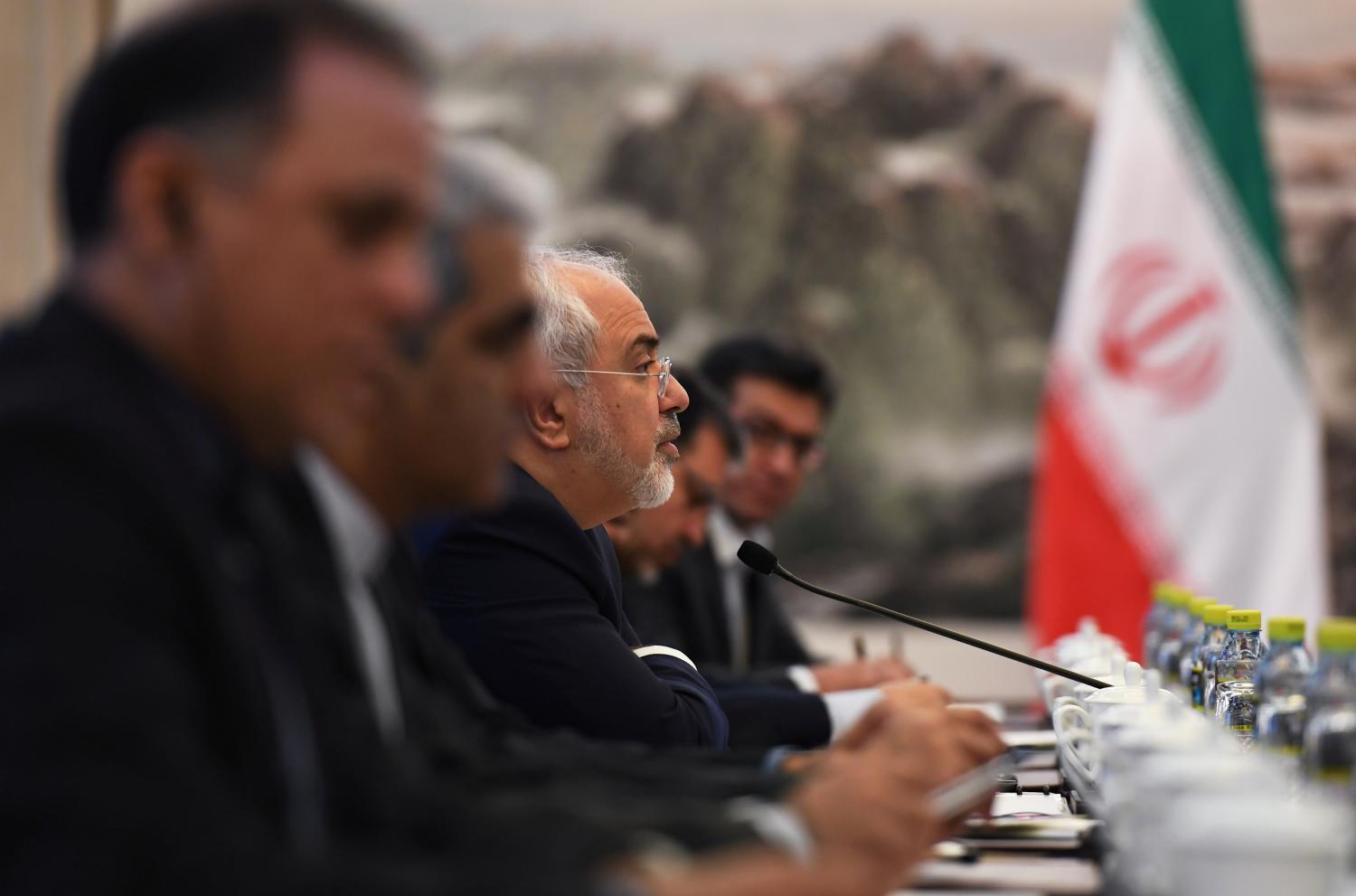
Was the Iran nuclear deal, signed last summer, a prelude to proliferation across the Middle East? This is a question that Brookings Senior Fellow Robert Einhorn and Non-resident Senior Fellow Richard Nephew explore in a new report. At an event to discuss their findings—moderated by Brookings Deputy Director of Foreign Policy and Senior Fellow Suzanne Maloney and with panelists Derek Chollet and H.E. Yousef Al Otaiba—Einhorn and Nephew argued that none of the Middle East’s “likely suspects” appears both inclined and able to acquire indigenous nuclear weapons capability in the foreseeable future. They also outlined policy options for the United States and other members of the P5+1.
Einhorn described the incentives and capabilities of Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates for acquiring nuclear weapons. He argued that, while both Saudi Arabia and the UAE a) consider Iran a direct military threat, b) have concerns about the U.S. commitment to the security of the region, and c) have sufficient financial resources, they recognize that they have no choice but to rely on the United States for their security and are unwilling to jeopardize that relationship by seeking nuclear weapons. Einhorn also said that both Egypt and Turkey do not view Iran as a direct military threat and are more preoccupied with instability on their borders and internal security, concerns that cannot be addressed by possession of a nuclear weapons capability.
Nephew outlined policy recommendations, including measures to ensure strict implementation of the JCPOA, greater intelligence sharing and security cooperation with Middle East allies, and means of fostering IAEA-supervised regional arrangements that would encourage peaceful nuclear energy development and limit potentially destabilizing nuclear activities. Nephew also asserted that some elements of the JCPOA, such as online monitoring of nuclear facilities, could be applied to other nuclear energy programs in the region to enhance transparency.
Derek Chollet of the German Marshall Fund argued the United States must deter Iran and reassure U.S. allies by maintaining a robust military presence in the region, planning a range of U.S. responses to destabilizing Iranian activities, and ensuring that U.S. forces have the weapons systems and personnel required for scenarios involving Iran. He suggested that the United States and its Middle East allies continue regular summit meetings on security and broader partnership issues, and possibly formalize security cooperation by establishing a dedicated regional security framework.
Emirati Ambassador to the United States Yousef Al Otaiba emphasized that, to many of the countries in the region, Iran poses a threat wider than just its nuclear activities. He suggested that the JCPOA will be judged on the degree to which the United States and its allies address Iran’s destabilizing behavior outside of the nuclear file, such as Tehran’s support for Hezbollah and the Houthis, as well as its ballistic missile activities. Al Otaiba said that, though he has seen some efforts by the Obama administration to push Iran on its regional behavior, it has sent a mixed message overall, with senior U.S. officials also encouraging European banks to invest in Iran. The ambassador asserted that rigorous enforcement of the JCPOA will be critical to convincing Iran not to eventually proceed to build nuclear weapons.
On Saudi Arabia, Einhorn noted that although the Obama administration supported the Saudi military campaign in Yemen, there was a risk that the Kingdom would overreact to its regional security challenges. He suggested that the United States pursue a dual-track approach: counter provocative Iranian behavior and defend the security interests of its regional partners, while at the same time seeking a resolution of regional disputes and encouraging Saudi Arabia and Iran to find ways of reducing tensions between them.
On the possibility that Iran would rapidly scale up its enrichment program, Einhorn acknowledged that while Tehran can legally do so under the JCPOA in 10 to 15 years, it will not have a strong civil nuclear rationale since it will be able to acquire nuclear fuel from Russia and other suppliers. Furthermore, Iran’s progress in centrifuge research and development may not be as rapid as Iran currently anticipates. Moreover, even if Iran elects to ramp up its enrichment program down the line, the JCPOA and Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) will bar it from pursuing nuclear weapons, and monitoring arrangements still in place will provide warning and enable the United States to intervene and prevent Iran from building nuclear weapons.
On reaching a regional accommodation that includes Iran, Al Otaiba indicated that the UAE would have much to gain, especially economically, from a better relationship with Tehran. He said the UAE and others in the region would like to try to engage with Iran to reduce tensions—but Iran, for its part, seems unwilling.
On prospects for a U.S.-Saudi civil nuclear cooperation agreement, Einhorn said that progress on such an agreement has stalled due to Saudi reluctance to formally renounce enrichment, something the United States has so far insisted on. He suggested that Washington should be prepared to relax the so-called “gold standard” (i.e., a formal renunciation of on enrichment and reprocessing) and instead accept an approach that would still discourage Saudi fuel cycle programs, such as giving Riyadh the right to pursue enrichment but allowing the United States to cease its nuclear cooperation if the Kingdom exercised that right. On the UAE’s civil nuclear program, Al Otaiba affirmed that the Emiratis continue to value the “gold standard” barring enrichment which is enshrined in the U.S.-UAE civil nuclear agreement, and have no plans to change their position on enrichment.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).










Commentary
The Iran deal and regional nuclear proliferation risks, explained
June 6, 2016