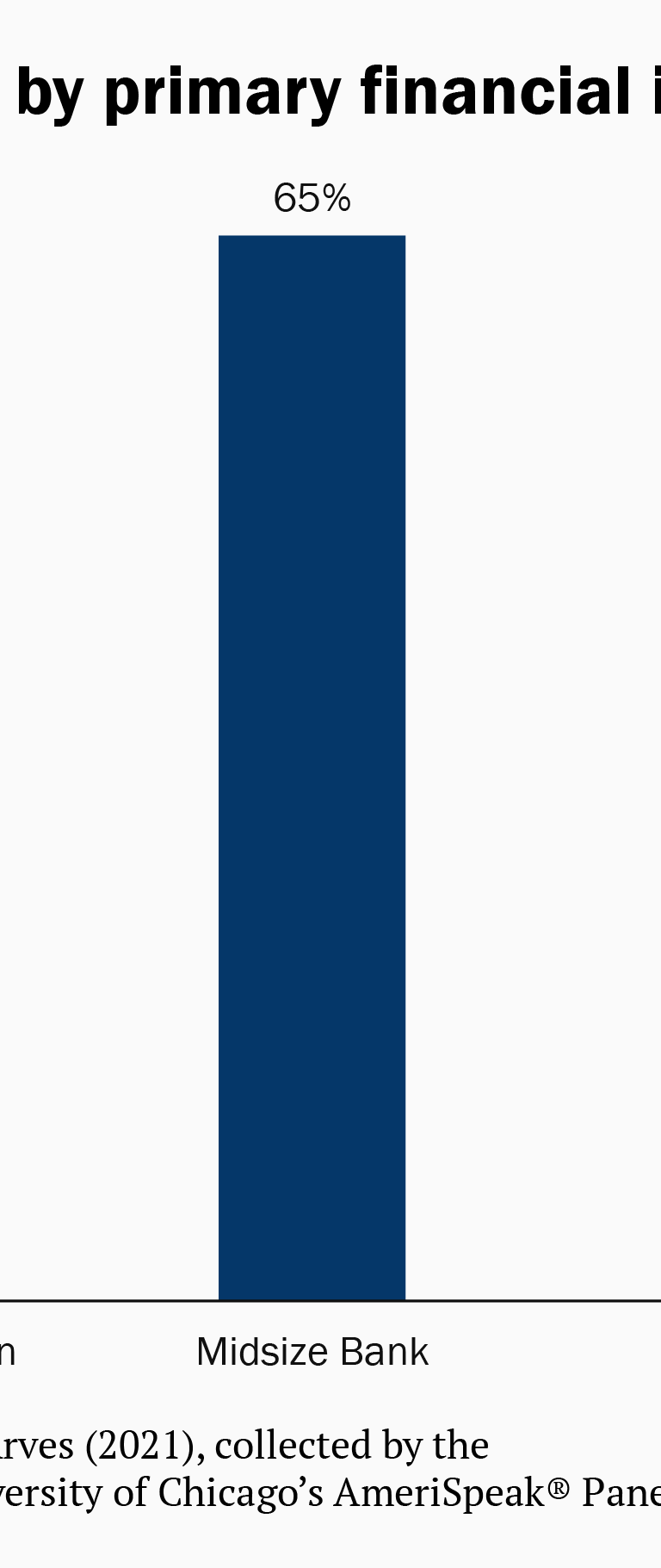After years of inactivity, momentum is gathering for policy action on issues related to consumer financial data in the United States. In July, the president issued an executive order encouraging the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) to enable data portability in financial services. The CFPB issued an advance notice of proposed rulemaking last year and expects to commence a rulemaking process in spring 2022. Congress has shown interest in the subject as well, most recently by holding a Task Force on Financial Technology hearing on consumers’ right to access financial data.
Such momentum is long overdue. Data portability in financial services has the potential to help consumers in their choice of financial service provider and enable innovation by new entrants seeking to offer a better deal or a novel product or service. While data portability is necessary to realize a more competitive and innovative financial services sector, other consumer data rights and protections are also needed. Our research indicates that consumers are demanding greater control than the current legal and regulatory framework governing financial data provides. To be responsive to these important interests, both regulatory and legislative action is needed to ensure that consumers have appropriate data rights and protections.
Background
In the wake of the global financial crisis and the ensuing public outrage over the behavior of “too big to fail” banks, policymakers in the early 2010s found themselves looking for ways to promote competition in financial services. While many debated the merits of breaking up large banks or a new Glass-Steagall Act to separate retail and investment banking, others looked for ways to promote competition from the ground up. Around the world, policymakers began to contemplate data portability measures as a way to loosen banks’ hold on dissatisfied customers.1
In the United States, this responsibility fell to the CFPB. Under Section 1033 of the Dodd Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010, the CFPB was empowered to prescribe rules to enable data portability in financial services.2 However, with numerous other priorities on the CFPB’s to-do list, rulemaking on Section 1033 never took place. Instead, the CFPB issued non-binding principles for data sharing and closely monitored developments in the market.
Meanwhile, consumer demand for data portability accelerated, driven by the burgeoning fintech revolution. To meet this demand, “data aggregation” companies such as Plaid began to connect consumers’ favorite fintech apps to their bank accounts. Data aggregators often used online banking login credentials shared by consumers to gain entry to consumer accounts and “screen-scrape” data available to consumers via online banking portals. Though this practice is still in use, aggregators have more recently begun to enter into contracts with banks, credit unions, core technology providers, and others to lessen dependence on credential-sharing and screen-scraping in favor of the use of tokenized account access and application program interfaces (APIs).
The financial data sharing ecosystem largely built on this technological framework has given rise to a vibrant fintech market, including many innovative companies who use consumer financial data to design products and services that help consumers improve their financial health. Today, fintechs offer products that use consumers’ financial data to help them avoid costly overdraft fees when their balances dwindle, build emergency savings when their balances grow, and optimize their bill payments to ensure that bills are paid on time without creating a liquidity shortfall. Other fintechs use cashflow data for underwriting purposes, a practice that shows evidence of increasing access to credit among those without a credit history or a credit score and those whose credit scores understate their creditworthiness.3 Still other fintechs use financial data to enable their customers to send money to friends and family within and between countries. These services are widely used, and their popularity has only increased as more and more banking activity moved online during the COVID-19 crisis.
In early 2021, the Financial Health Network conducted a nationally representative survey to explore consumers’ interactions with, and attitudes towards, the financial data ecosystem. According to our research, more than two thirds of banked consumers are fintech users, having linked financial apps to their checking account. In contrast with banks and credit unions,4 young people and people of color are particularly likely to use fintech apps, with apps used to send money to friends and family being the most common type of fintech app and the type of fintech app used most frequently.
The need for data portability
The lack of a comprehensive legal framework designed to govern the rights and duties of the various players in this ecosystem creates risks for individual consumers, financial institutions, and the functioning of the financial data ecosystem as a whole. Last year, the Financial Health Network partnered with FinRegLab, Flourish Ventures, and the Mitchell Sandler law firm to produce a comprehensive analysis of the legal and regulatory landscape governing consumer financial data. This analysis uncovered numerous open interpretive and policy questions related to Section 1033 as well as older statutes covering a set of interlocking issues including privacy and security under the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, accuracy and privacy under the Fair Credit Reporting Act, fairness under the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, and liability under the Electronic Funds Transfer Act.
Unless regulators take action, these open questions will continue to fester and have the potential to impede data portability. Already there are reports of some financial institutions restricting access to consumer data.5 Such restrictions can serve to entrench incumbent institutions and limit competition to the detriment of consumers. These restrictions also are out of step with consumer preferences. According to our research, 62 percent of consumers are in favor of data portability, believing that their bank or credit union should be required to share their personal data with another company (such as a fintech provider) if the consumer directs it to do so.
Importantly, this majority holds across demographic groups, including age, gender, education, race/ethnicity, and household income. Support for data portability in financial services is also bipartisan, with majorities of self-identified Democrats, Republicans, and Independents in favor of it.
Support for data portability holds regardless of the type of institution that serves as a consumer’s primary bank or credit union. This underscores the importance of ensuring that customers of small financial institutions with more limited technological resources have access to secure, affordable solutions to enable data portability.
These results confirm a broad consensus in favor of data portability that has been increasingly apparent for some time. Indeed, at the CFPB’s Symposium on Consumer Access to Financial Records in early 2020, few participants disputed that data portability is a right that should be available to consumers and that rulemaking on Section 1033 should guarantee.6 What they did not agree on was what other rights and protections should be guaranteed and how best to do so.
The data minimization principle
Among the issues dividing large banks, small banks, fintechs, data aggregators, and other market participants at the CFPB’s 2020 Symposium was the question of the scope. What kind of data fields should be able to be shared under Section 1033, and who should decide what kind of data are appropriate for what use case?
In the absence of regulatory guidance, the scope of data available to be shared at a consumer’s direction today varies greatly depending on where a consumer banks. Practically, this means that while some consumers currently enjoy a high degree of data portability, others have a much more limited ability to consistently share their data. As a result, consumers are unlikely to understand the scope of the data they share unless they carefully read complex legal disclosures.
The Financial Health Network asked fintech app users who had connected their fintech app to their checking account how much of their checking account data their fintech app is capable of accessing. 41 percent reported believing it could only access the data it needed, 25 percent reported believing it could access all of their checking account data, and the remaining third of respondents reported that they did not know.
When asked about how much of their checking account data fintech apps should be able to access, 87 percent reported believing that their fintech app should only be able to access the data it needs. Only 11 percent reported believing it should be able to access all the data in their checking account. In other words, consumers know what rules they want, but they are not sure if the current system is aligned with their preferences.
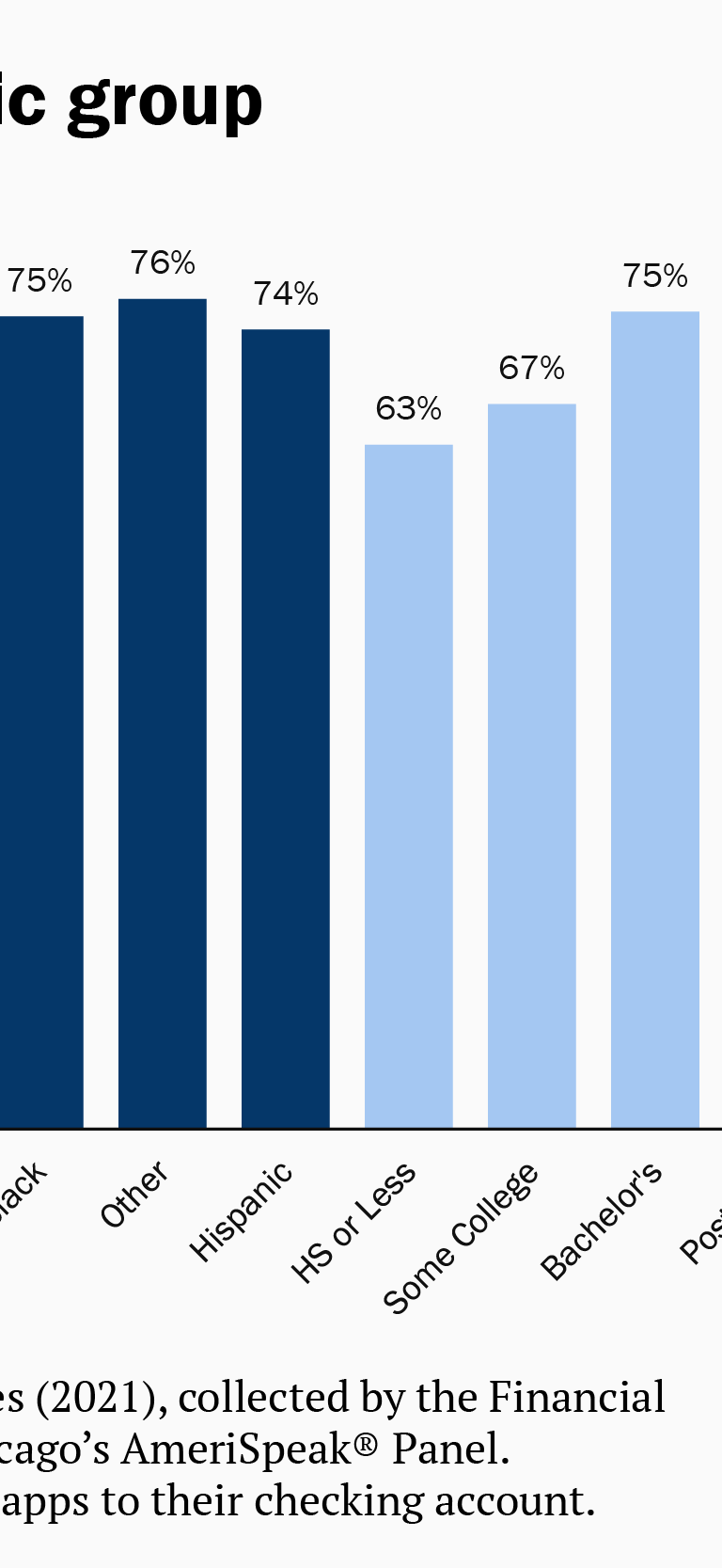
As with data portability, this preference for data minimization holds across demographic groups, including age, gender, education, race/ethnicity, household income, and political party affiliation. Unlike data portability, the preference for data minimization is overwhelming, with support usually in the high 80s to low 90s, with at least 75 percent of each demographic group in favor.
This indicates that while consumers desire the right to data portability, they have a strong preference for discretion as they share their data and do not wish to share any data beyond what is required for a given use case. Some data holding financial institutions (such as banks) have also emphasized this data minimization principle. However, those entities have their own competitive incentives to limit data flows and would not be impartial arbiters of what data are needed for a given use case.
With this market dynamic in mind, the CFPB should use its authority under Section 1033 to determine what data must be accessible, how often they must be made available, how long those data can be accessed for, and to whom they may be made available. If the CFPB does not feel it has the authority to impose data minimization limitations on data aggregators and recipients without impeding data portability, further legislative action may be needed to empower the Bureau to ensure that those entities are only accessing the data they need for a given use case, and are only storing that data for the minimum amount of time necessary. Congress will find strong support for this principle across the political and socio-economic spectrums.
Protecting consumers’ privacy
Consumers’ preference for discretion is not limited to the data they choose to share with fintech apps. Indeed, our research indicates that consumers are equally sensitive to financial or personal data about them being shared without their affirmative consent, no matter what institution is doing the sharing. Just as consumers do not want big tech companies sharing data about their browsing patterns without consent, consumers likewise do not want their bank or fintech app sharing financial data about them without their consent. Our survey shows consumers seem to view these forms of data sharing in much the same way, despite other research indicating that consumers have differing levels of trust for these institutions more broadly.7
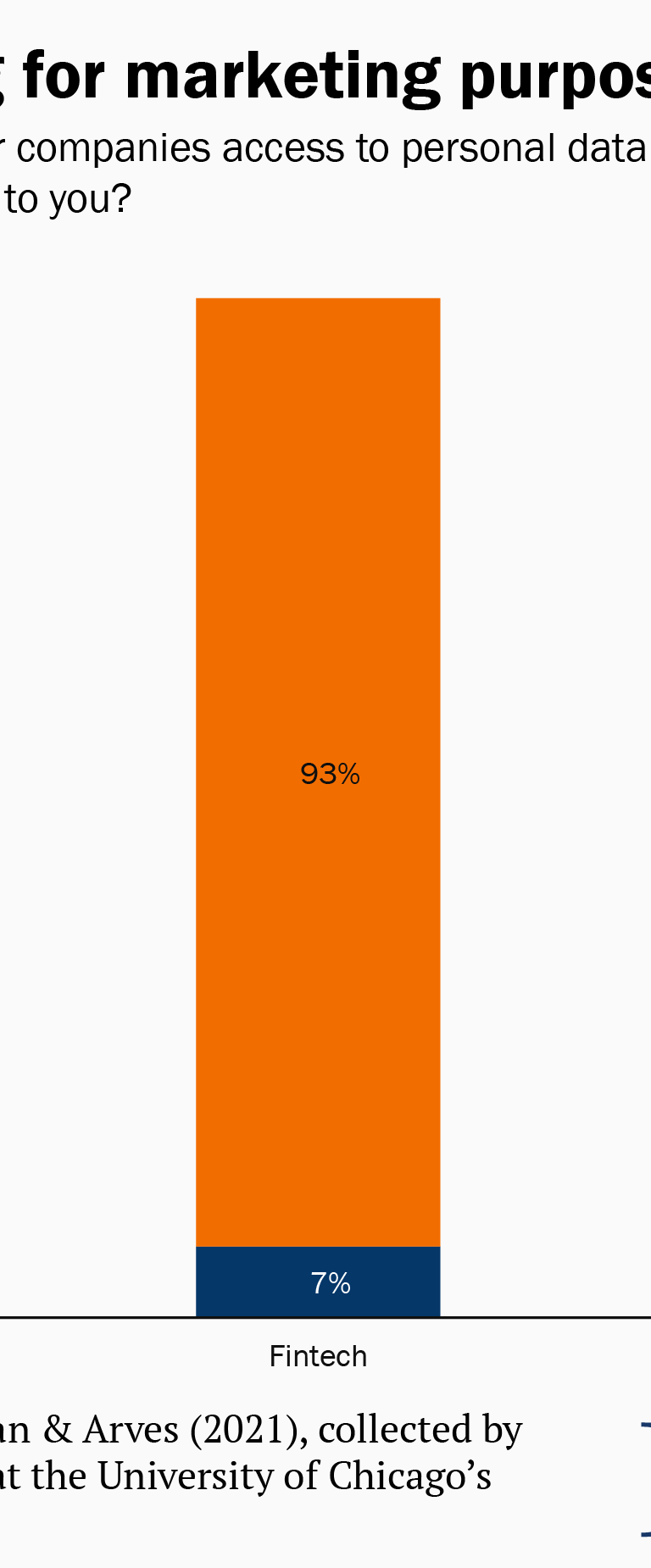
Almost 90 percent of consumers (consistent among all demographic groups) expressed a preference for data sharing by their primary bank or credit union to be bound by an opt-in standard rather than an opt-out standard.
This strong preference for an opt-in standard stands in sharp contrast with current legal requirements which cannot be changed without legislative action. At present, consumers who do not want their data to be shared must opt-out, and even their ability to do that is limited. Banks are still permitted under the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act to share consumer data with non-affiliated third parties if the information sharing is subject to one of the numerous exceptions under the law, regardless of whether a consumer might prefer them not to share.8 In other words, the current law places the burden of protecting privacy on consumers, who are expected to carefully parse complex legal disclosures provided by their financial institution and affirmatively opt-out of any optional data sharing. According to our research, only about 1 in 4 consumers reports having done this. As low as that is, it may under-state how rare it is for consumers to opt-out of data sharing. The plurality of banks interviewed in a 2020 study by the Government Accountability Office reported opt-out rates less than 5 percent.
In order to ensure that privacy protections are reflective of consumers’ preferences, we believe that legislative change is needed. The United States is past due for comprehensive data privacy legislation that not only addresses open issues in financial services but also ensures that consumers are afforded strong and consistent data rights and protections when they interact with tech platforms, healthcare providers, educational institutions, and others. However, if such a comprehensive effort remains beyond the reach of Congress, lawmakers should nevertheless build on the bipartisan consensus among consumers and past interest from both Republicans and Democrats in updating consumers’ data rights and protections in financial services. At the very least, data sharing by financial institutions should be bound by an opt-in standard.
Conclusion
As the financial data ecosystem evolves, regulatory and legislative action to ensure that consumers have strong data rights and protections is increasingly urgent. With momentum for action building and consumers having an unusual level of agreement on the need for data portability, data minimization, and data privacy, policymakers should proceed with the clear goal of ensuring that consumers are the primary beneficiary of the use of their financial data.
-
Footnotes
- Retail Banking Market Investigation: Final Report; Competition and Markets Authority; 2016.
- Dodd-Frank Act Section 1033 – Consumer Access to Financial Records; Consumer Financial Protection Bureau
- The Use of Cash-Flow Data in Underwriting Credit; FinRegLab
- How America Banks: Household Use of Banking and Financial Services; Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, October 2020
- Venmo Glitch Opens Window on War Between Banks, Fintech Firms; The Wall Street Journal; December 2019
- CFPB Symposium: Consumer Access to Financial Records, Consumer Financial Protection Bureau
- Edelman Trust Barometer 2021, Edelman, March 2021; Fintech Apps and Data Privacy: New Insights from Consumer Research, The Clearing House, August 2018.
- Consumer Financial Data: Legal and Regulatory Landscape; Financial Health Network, FinRegLab, Flourish Ventures, & Mitchell Sandler; 2020
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).