Abstract
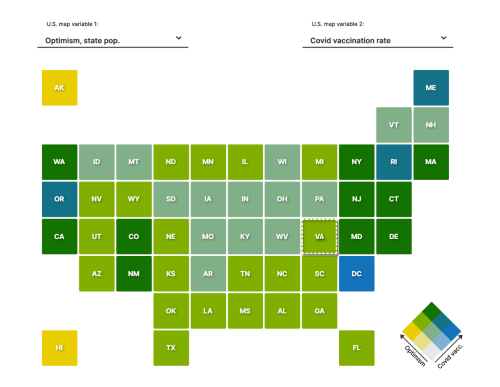
We use Gallup World Poll data from over 150 countries from 2009-2019 at both the individual and country levels to revisit the relationship between income and subjective wellbeing. Our inspiration is the paradox first proposed by Easterlin (1974), according to which higher incomes are associated with greater happiness in cross-sections, yet increases in a country’s GDP per head do not increase its average wellbeing. In our analysis subjective wellbeing (or happiness) is measured by the Cantril ladder on a 0-10 scale. Across individuals, other things equal, one unit of log income raises subjective wellbeing by 0.4 points. In other words, doubling income raises wellbeing by 0.3 points out of 10. Across countries, a crude regression of log income on per capita income gives a higher coefficient of 0.6. But, once social variables like health and social support are introduced, the picture changes. In rich countries, income no longer has a significant effect, either in country cross-sections or in time series: higher income only matters due to its correlation with the social variables. For low-income countries the result is also clear cut – income raises happiness in both cross-section and time series, whether the social variables are controlled for or not. For middle-income countries the result is mixed.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).