From its modest beginnings in 1975, the Earned Income Tax Credit has grown into one of the nation’s most effective anti-poverty programs. Each year, the EITC supplements low-income workers’ earnings, encouraging work and lifting millions of people out of poverty.1 It has positive lasting effects for parents, who have shown longer-run earnings increases and better health outcomes. At the same time, their children exhibit a host of benefits, from better school performance and higher rates of college enrollment to more hours worked and higher incomes in adulthood.2
Moreover, the EITC supports economic stability in communities throughout the country where filers collectively receive millions of dollars in earnings supplements annually.3 These successes stem from a series of targeted expansions—supported by both Republicans and Democrats—over the EITC’s 40-year history, transforming it from a small credit into a significant income supplement for low-income working families.4
Yet more can be done to preserve and build on the effectiveness of the EITC, and a growing number of elected officials and policy experts have proposed strengthening the credit. Three main recommendations have emerged from these proposals.
Preserve two key provisions of the EITC that are set to expire in 2017;
Expand the credit for workers without qualifying children; and
Offer filers options to receive a portion of the credit outside of tax time.
In this brief, we consider the first two recommendations, using our MetroTax model and detailed microdata from the 2014 American Community Survey to estimate the impact of these potential changes on workers and on the metropolitan areas and states where they live.5 A new analysis by Steve Holt will take an in-depth look at the issue of periodic payment.
If two key EITC provisions expire in 2017, 7.4 million filers would lose part or all of their EITC.
In 2009, Congress and the Obama administration enacted two targeted, but temporary, expansions to the EITC. The legislation reduced the “penalty” for married couples filing jointly by extending their eligibility for the credit $5,000 beyond that for unmarried filers, and it boosted the credit for families with three or more children (who are more likely to be low-income even when working).
If those provisions expire in 2017, the EITC would shrink for 6.7 million taxpayers, while a little under 700,000 filers would lose eligibility altogether. Two-thirds of filers who would be affected are married couples, 1.8 million of whom are also raising more than two kids (meaning they would be subject to both cuts). The remaining third are unmarried workers with at least three children. Most of these taxpayers (58 percent) have a high school diploma or less, and they are most likely to work in manufacturing, construction, and retail. The typical adjusted gross income of these filers is $28,000 a year, just above the poverty line for a family of four (roughly $24,000 in 2014).
States and metro areas in the Midwest and West would see the steepest cuts if these provisions expire.
Every state stands to lose millions of dollars if these EITC provisions are not made permanent. States and metro areas with higher-than-average shares of married couples and larger families would be hardest hit. In the Intermountain West, Idaho and Utah could see a 10 percent drop in federal EITC dollars coming into the state (Table 1). The major population centers in those states—including metropolitan Provo and Ogden in Utah and Boise, Idaho—top the list of major metro areas that would experience the biggest cuts if these provisions expire.
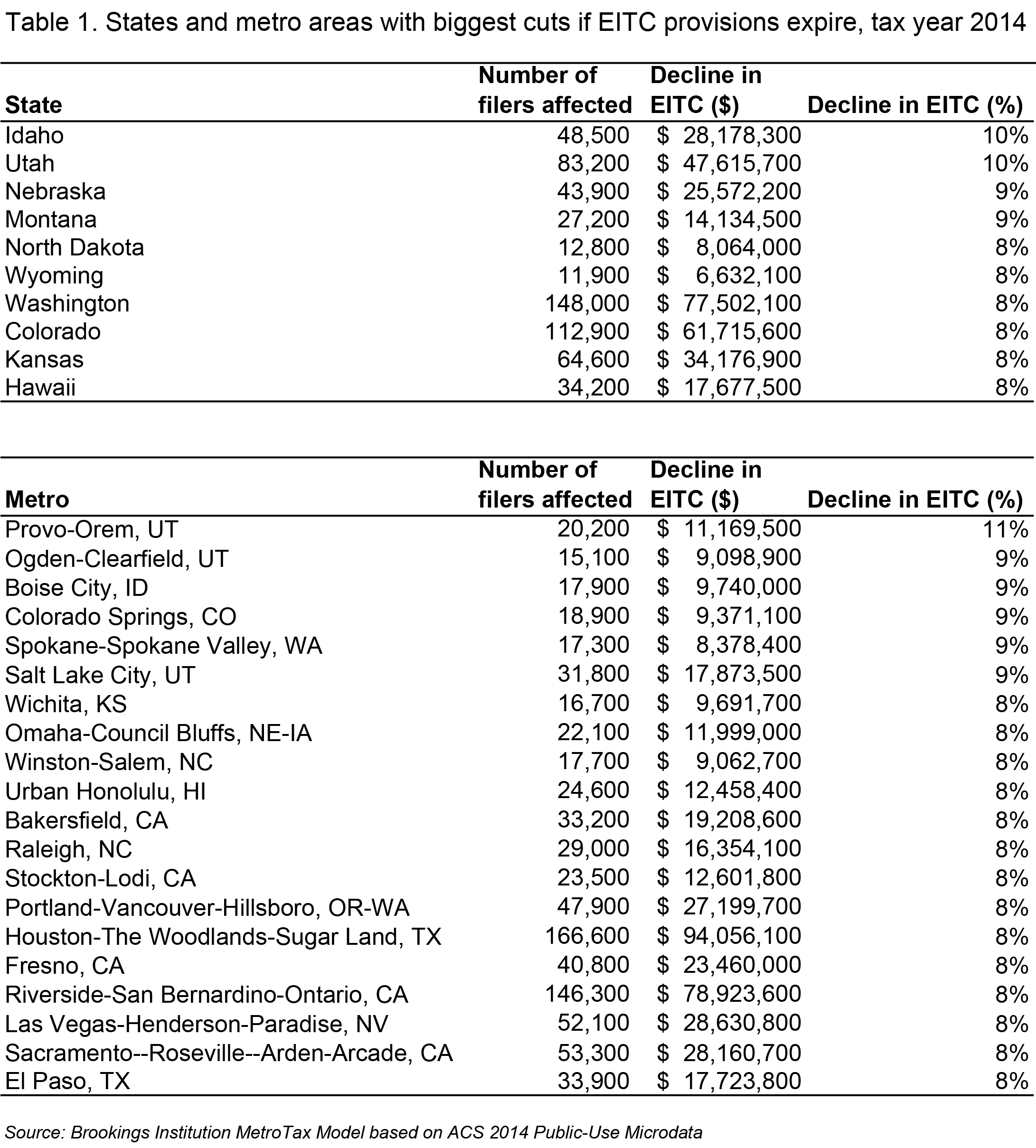
While larger states like California and Texas would see their EITC claims drop by smaller percentages, the size of the EITC-eligible population in these states mean that the expiration of these two provisions would translate into a loss of more than half a billion dollars in California ($538 million) and over $400 million in Texas. Taxpayers in the Los Angeles metro area stand to lose an estimated $185 million in EITC receipts, while those in Dallas would forfeit nearly $100 million. (For detailed state and metro data see the appendix.)
Expanding the credit for workers without qualifying children would benefit more than 14.4 million filers.
The EITC for childless workers is significantly smaller than the credit for families with children. In tax year 2013 (the most recent year for which detailed data are available), workers with qualifying dependents received $2,794 on average through the EITC, compared to the meager $281 claimed by the average childless worker.6 In fact, low-wage earning childless adults are the only group of taxpayers actually taxed into (or deeper into) poverty by the federal tax system.7
Both President Obama and House Speaker Paul Ryan have proposed expanding the EITC for these workers, as have legislators—including Sen. Patty Murray (D-Wash.), Rep. Richard Neal (D-Mass.), and Rep. Barbara Lee (D-Calif.)—and Republican presidential candidate Jeb Bush.8 (Republican presidential candidates Ted Cruz and John Kasich have also called for the EITC to be expanded but have not specified whom that expansion would target.9)
The proposals put forward by Obama, Ryan, Lee, and Bush are strikingly similar (although they differ considerably in how they would pay for it). These expansions would double the size of the credit for childless workers and the pace at which the credit phases in and out (Figure 1). They would also lower the minimum age of eligibility from 25 to 21.10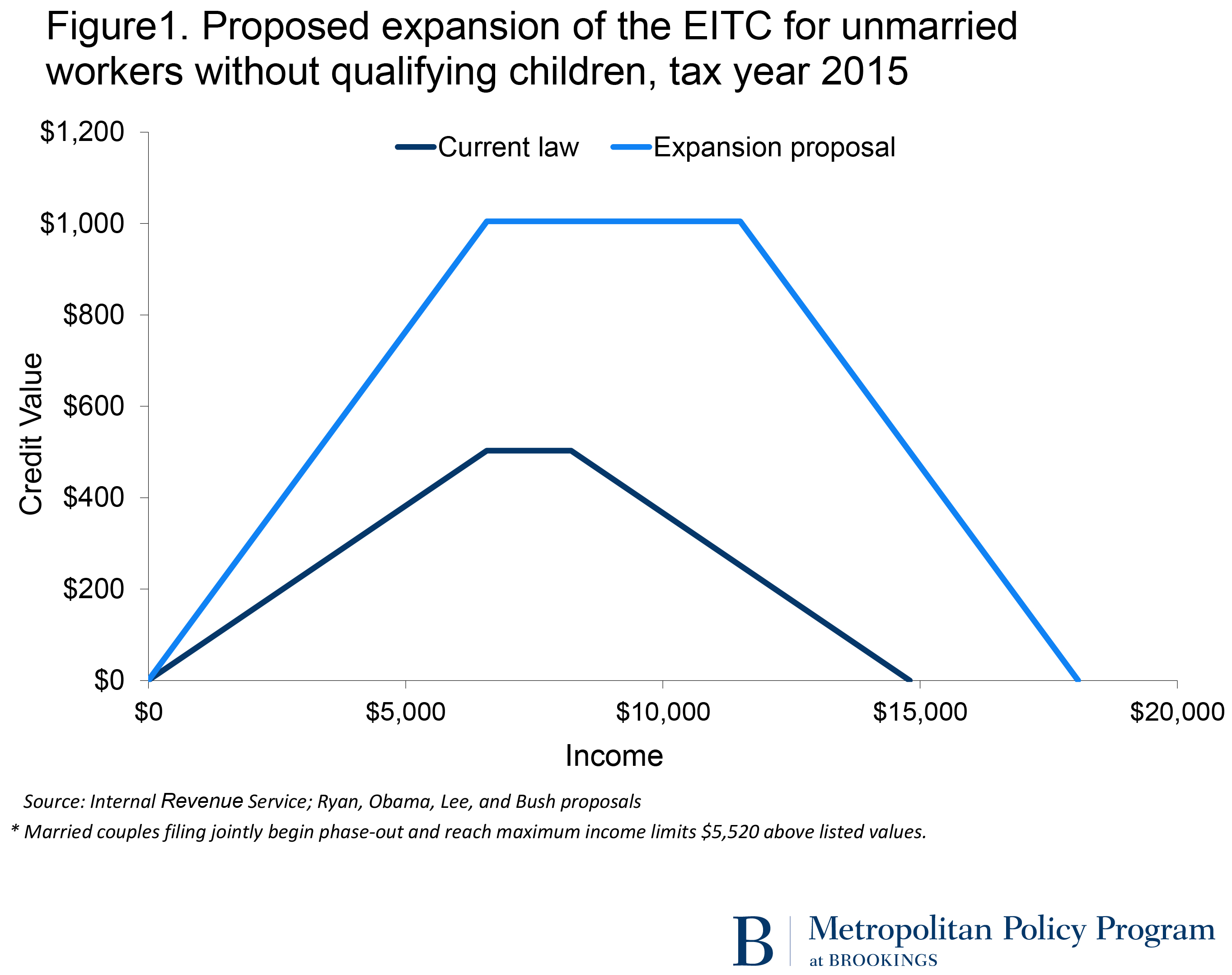
Together, these changes would boost the value of the credit for 8 million filers and extend eligibility to 6.4 million more taxpayers, increasing EITC dollars for these workers by $6.9 billion.11
The filers who would benefit from these changes are largely unmarried workers (87 percent) who are most likely to be employed in service industries (retail, accommodation and food service, administrative services), health care, and construction. Half of these workers have a high school diploma or less. The typical adjusted gross income for these workers is just $8,300, well below the poverty threshold for individuals and married couples without children (e.g., $12,316 and $15,853, respectively, in 2014).
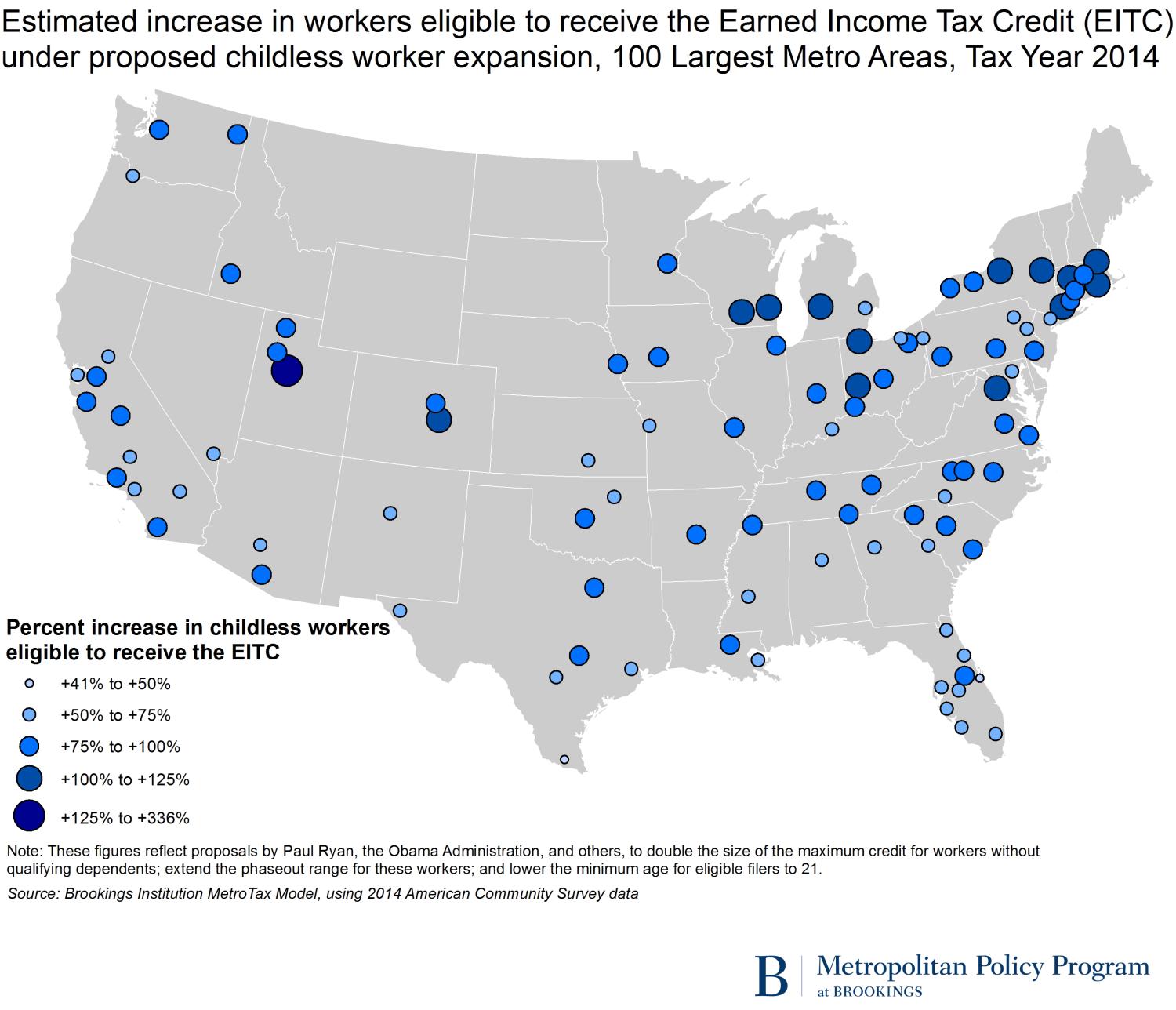
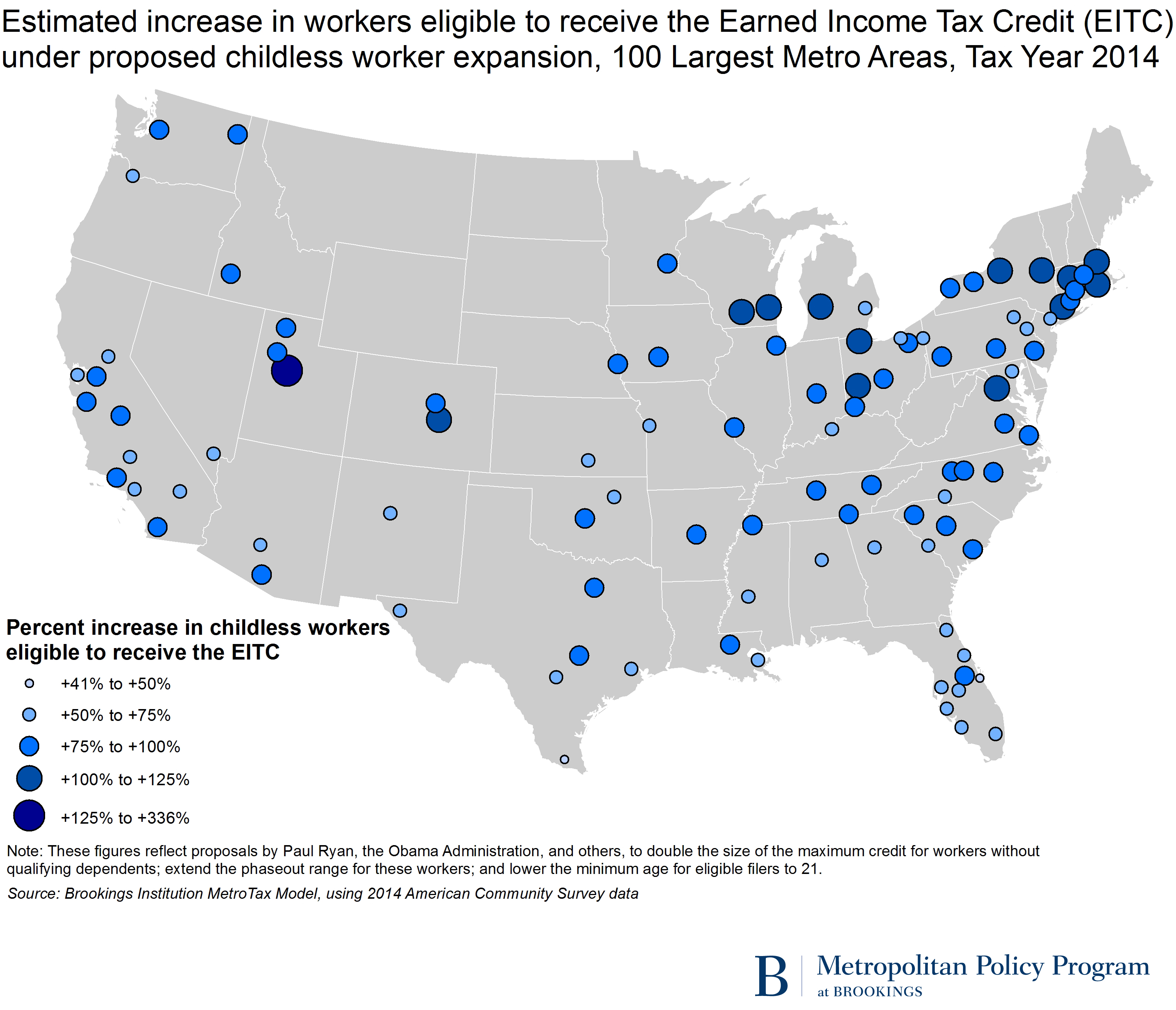
Several states and large metro areas in the Midwest and Northeast would see the number of childless workers eligible for the EITC more than double if the credit were expanded.
The District of Columbia and Utah, each of which has above-average shares of the population between 21 and 24, would experience the largest percentage growth in the number of childless workers eligible for the EITC (135 and 134 percent, respectively). However, the bulk of states that would double their pool of eligible filers without qualifying children fall in the Midwest (North Dakota, Iowa, Nebraska, and Wisconsin) and Northeast (Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and Vermont), and tend have higher-than-average shares of one-person households and households without children.
Similarly, while the number of EITC-eligible childless workers in the Provo metro area would more than triple if the credit were expanded, most of the major metro areas that would at least double the number of eligible workers without qualifying children are in the Midwest (e.g., Grand Rapids, Milwaukee, and Toledo) and Northeast (e.g., Bridgeport, Boston, and Springfield) (Map 1).
In this era of partisan gridlock in Washington, it is rare to find a policy with the kind of bipartisan support the EITC has received—a testament to its effectiveness in encouraging work, alleviating poverty, and improving outcomes for workers and their children. By preserving key provisions of the EITC for working families and by making the EITC work better for workers without qualifying children, millions of Americans across the country stand to benefit.
Notes
1. See brookings-edu-2023.go-vip.net/blogs/the-avenue/posts/2014/12/16-poverty-tax-eitc-kneebone-holmes.
2. Chuck Marr, et al., “The EITC and Child Tax Credit promote work, reduce poverty, and support children’s development, research finds,” (Washington: Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, 2015).
3. See http://www.gistfunders.org/documents/GCYFInSightFall2015.pdf.
4. In 1975 the maximum credit for workers with children was $400. In tax year 2015, the maximum credit amount ranges from $3,359 to $6,242, depending on the number of children.
5. For more information on the MetroTax model, see the technical appendix: brookings-edu-2023.go-vip.net/~/media/Research/Files/Reports/2008/6/05-metro-raise-berube/metroraise_technicalappendix.PDF.
6. For more detailed data on filers and credit amounts by number of qualifying children, visit EITC Interactive at brookings-edu-2023.go-vip.net/research/interactives/eitc.
7. Chuck Marr, et al., “Lone group taxed into poverty should receive a larger EITC,” (Washington: Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, 2014).
8. Office of Management and Budget, “Fiscal Year 2016 Budget of the U.S. Government,” (Washington: OMB, 2015), available at https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/default/files/omb/budget/fy2016/assets/budget.pdf; House Budget Committee, “The Path to Prosperity: Fiscal Year 2015 Budget Resolution,” (Washington: HBC, 2014), available at http://budget.house.gov/uploadedfiles/fy15_blueprint.pdf; Senator Patty Murray, “21st Century Workers Tax Cut Act,” S.660; Representative Richard E. Neal, “Earned Income Tax Credit Improvement and Simplification Act 2015,” H.R. 902; Representative Barbara Lee, “Pathways Out of Poverty Act of 2015”, H.R. 2721.
9. Tax Credits for Working Families, “The 2016 Presidential Race,” http://www.taxcreditsforworkingfamilies.org/the-2016-presidential-race-where-the-candidates-stand-on-tax-credits/; Tax Foundation, “Comparing the 2016 Presidential Tax Reform Proposals,” http://taxfoundation.org/comparing-2016-presidential-tax-reform-proposals.
10. President Obama and Rep. Lee also recommend raising the maximum age of eligibility to 67 to harmonize the credit with increases in Social Security’s full retirement age.
11. Raising the maximum age to 67 would benefit an additional 362,000 workers and increase the total EITC amount by another $232 million.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).