There is a marriage gap in America. This is not just a gap in choices and actions, but in norms and attitudes. Each generation is more liberal, on average, when it comes to issues like premarital relationships, same-sex marriage, and divorce. But generational averages can obscure other divides, including ideology—which in many cases is a more powerful factor.
Take opinions on the most important prerequisites for marriage, as explored in the American Family Survey conducted earlier this year by Deseret News and the Center for the Study of Elections and Democracy (disclosure: I am an adviser to the pollsters). There is widespread agreement that it is best to have a stable job and to have completed college before tying the knot. But there is less agreement in the 3,000-person survey on other questions, including premarital cohabitation.
Living in sin, or preparing for commitment?
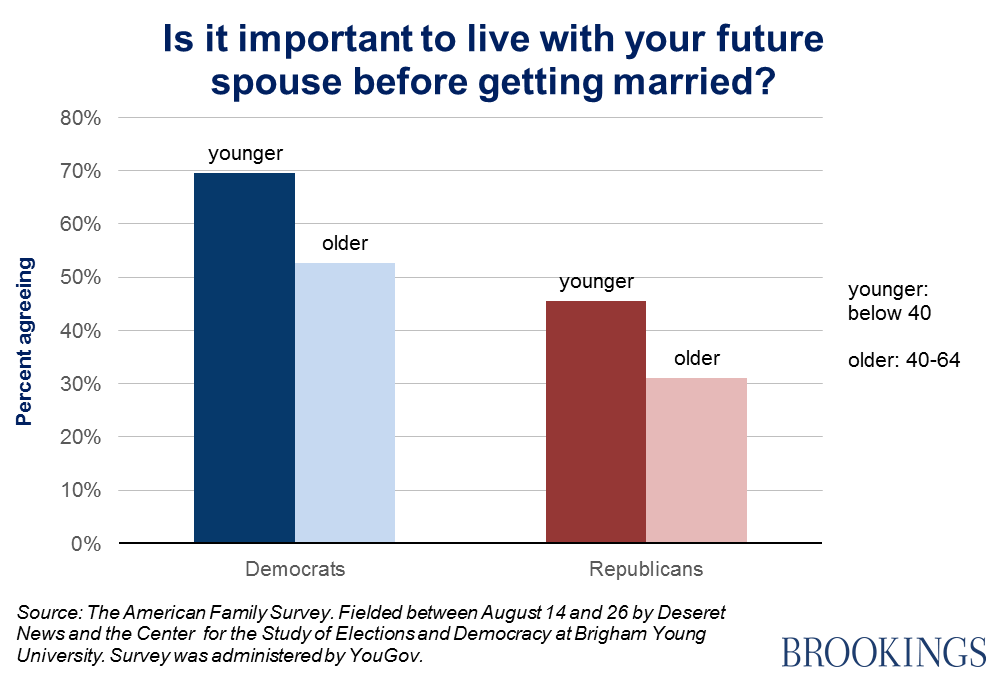
In response to the question of whether it is “important to live with your future spouse before getting married,” a clear gap emerges between those who identify as Democrats and those who identify as Republicans. This gap trumps the generational one, with younger Republicans (under 40) more conservative than Democrats over the age of 40:
The importance of family stability for a child’s wellbeing and prospects is well-documented, not least in Isabel Sawhill’s book, Generation Unbound. The question is not whether stability matters, but how best to promote it. To the extent that biological parents stay together and provide a stable environment, it doesn’t much matter if they are married. For children living with both biological parents, there is no difference in outcomes between those being raised by a married couple compared to a cohabiting couple, according to research by Wendy Manning at Bowling Green State University.
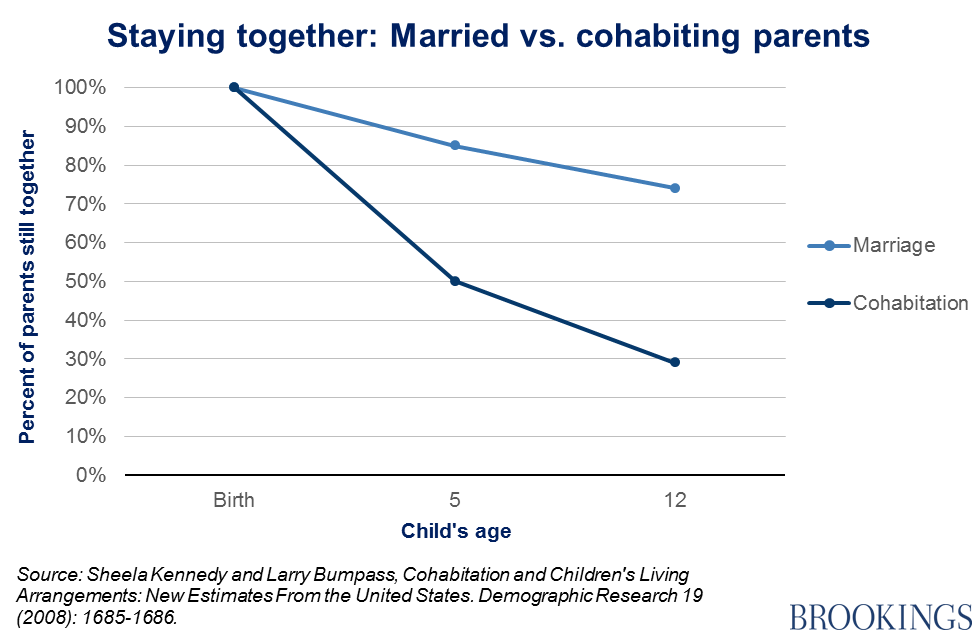
But people who marry are much more likely to stay together:
Marriage, at least in America, does seem to act as an important commitment device, a “co-parenting” contract for the modern world, as I’ve argued in an essay for The Atlantic, “How to Save Marriage in America.”
The varied meaning of “cohabitation”
Cohabitation can signal radically different situations. A couple who plan to live together for a couple of years, then marry, and then plan the timing of having children are very different from a couple who start living together, accidentally get pregnant, and then, perhaps somewhat reluctantly, get married.
There is some evidence that cohabitation is in fact becoming a more common bridge to marriage and commitment. First-time premarital cohabiting relationships are also lasting longer on average and increasingly turn into marriage: around seven in ten cohabiting couples are still together after three years, of whom four have married.
In the end what matters is planning, stability, and commitment. If cohabitation is a planned prelude to what some scholars have labeled “decisive marriages,” it seems likely to prove a helpful shift in social norms, by allowing couples to test life under the same roof before making a longer-term commitment. Sawhill’s distinction between “drifters” and “planners” in terms of pregnancy may also be useful when it comes to thinking about cohabitation, too.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).




Commentary
“Should we live together first?” Yes, say Democrats. No, say Republicans (even young ones)
May 19, 2016