Interpreting employment stats among young people can be tricky. No one expects employment rates among teens or people in their early 20s to reach those of prime-age workers. These are prime years for what economists call “investing in human capital,” an activity most people would describe as “going to school.”
Education requirements for good jobs are getting higher, so finishing high school and earning a post-secondary credential like two or four-year college degrees, apprenticeships, or certifications are top priorities. But early work experiences can allow young people to learn new skills, gain experience, and expand networks. Evidence suggests that it can improve employment prospects down the line. And the earlier that people are exposed to the workplace, the earlier they learn such skills as teamwork, communication, and dependability—skills that employers say are in short supply.
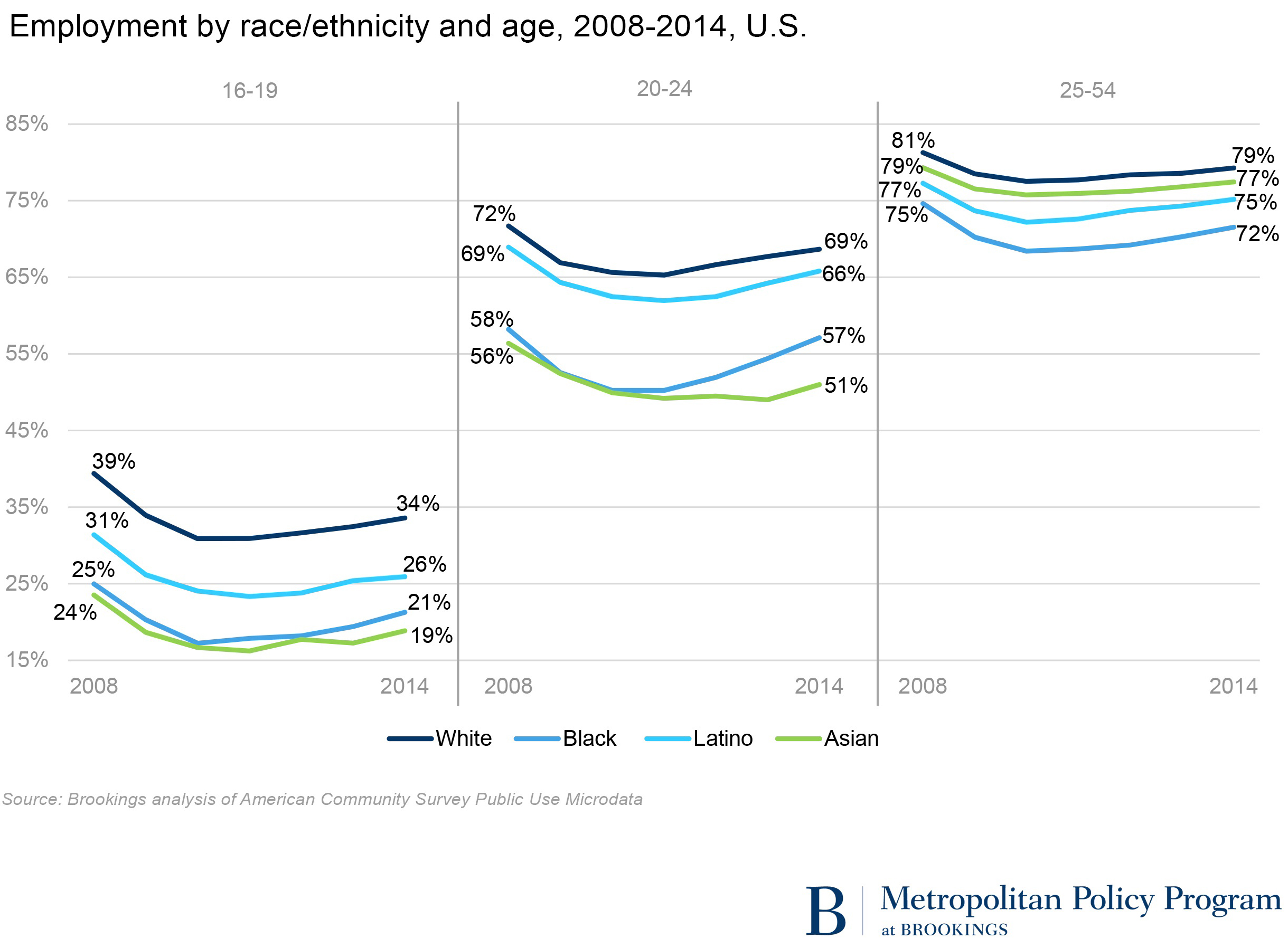
The employment rate for teens fell from 43 percent in 2000 to 26 percent in 2014, and for young adults aged 20 to 24, it fell from 70 to 62 percent. These are big drops. In a new analysis, I take a deeper look at employment trends among young people. When employment rates are broken out by age and race/ethnicity, you see the same downward pattern, but also substantial variation among whites, blacks, Latinos, and Asians.
Do these declines spell trouble? The answer is, it depends: on how young people spend their time, what resources and support are available to them, and how the person making the judgement values academics and enrichment relative to employment.
Some argue that workplace experience provides key developmental opportunities that benefit all young people. Robert Halpern, for example, wryly notes that high school students are isolated from the adult world “at just the moment when [they] need to begin learning about participating in it.”
Others say that employment matters more for some young people than others. For example, disadvantaged youth—those not on track to earn a post-secondary credential and without strong family or community networks to help them find jobs—can particularly benefit from formal programs that connect them to the labor market. As Jeylan Mortimer concluded about “low academic promise” high school students (those with poor grades and low educational goals): “[H]aving a positive work experience can help to turn you around. For those who have a lot of disadvantages, any positive experience is likely to have a greater impact than on people with a lot of advantages already.” Research on Career Academies, high schools that combine academics with career development, support this view. Career Academy students, disproportionately low-income, black, and Latino, posted significant earnings gains eight years after graduation, and young male graduates also had higher rates of marriage and custodial parenthood.
And some would say that it’s appropriate to prioritize education over employment, especially for teens, who are typically not responsible for supporting themselves and their families.
So what do the data tell us? Voluntarily dropping out of the labor force to concentrate on academics as a young person can pay off when people enter their prime working years, generally considered to be 25 to 54. Though education and work are not necessarily incompatible, employment rates are generally lower among students than among those not enrolled in school. Among teens and young adults, Asians have the lowest employment rates, but they also have the highest school enrollment rates. 92 percent of Asian 16- to 19-year-olds and 63 percent of Asian 20- to 24-year-olds are in school, compared to 80 percent and 38 percent among all races. It follows, then, that Asians have high levels of educational attainment. In fact, 50 percent of 23- to 24-year-old Asians have a Bachelor’s degree, double the average rate. Given the strong correlation between education and employment, it is not a coincidence that prime-age Asians have high employment rates and low unemployment rates. Their low employment rates as young people do not, on the whole, seem to lead to problems as adults. (Of course, this is not to downplay the diversity of the Asian population and to suggest that all Asians are doing well economically.)
On the other hand, blacks have the second lowest employment rates as teens and young adults, and the lowest rate as prime age workers. They also have the highest unemployment rates, showing an active desire to work. Among black teens in 2014, the unemployment rate was 38 percent, compared to 23 percent overall, and it was 22 percent among black young adults, compared to 13 percent overall. The trend continues into prime working years: blacks have an unemployment rate of 11.4 percent, nearly double the overall rate of 6.2 percent. The low employment rate among young black people is not driven by school enrollment. Latinos have similar (below-average) enrollment levels but higher employment rates, and whites have much higher employment rates but only slightly higher enrollment levels. The weaker employment outcomes of blacks at all ages is probably related to multiple factors: relatively low levels of educational attainment, discrimination, and the neighborhood effects of living in concentrated poverty.
Blacks and Latinos are disproportionately represented among so-called “disconnected youth,” young people aged 16 to 24 who are neither working nor in school. 17 percent of black young adults aged 20 to 24 are disconnected, as are 13 percent of Latinos, 7 percent of whites, and 4 percent of Asians. Half of disconnected young adults have a high school credential and another 20 percent have taken some college courses, suggesting that getting these young people on a better path involves not only reducing the high school dropout rate, but also strengthening the transition from high school to post-secondary education and the labor market.
In short, employment rates among young people tell different stories that often track by race and ethnicity. Some voluntarily withdraw from the labor market to focus on academics and extra-curricular activities, others would really like a job but can’t find one, and some—the most disadvantaged—are alienated from both school and the labor market.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).



Commentary
Decoding declines in youth employment
June 1, 2016