There’s at least one policy that both parties agree has been successful in combatting poverty: the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). And rightly so – in 2012, the EITC pulled 6.5 million people out of poverty, including around 3.3 million children. Politicians on both sides of the fence have put forward plans for expanding the EITC to unmarried childless adults, including President Obama and Rep. Paul Ryan who propose very similar expansions. As Dylan Matthews of Vox.com puts it: “Ryan’s proposal is almost identical to President Obama’s, included in his current budget; the only difference is that Obama would also increase the maximum age one can claim the EITC from 65 to 67.” There is however a large difference in the plans: how, and by whom, this expansion will be paid for.
Similarities in the Obama and Ryan EITC expansions
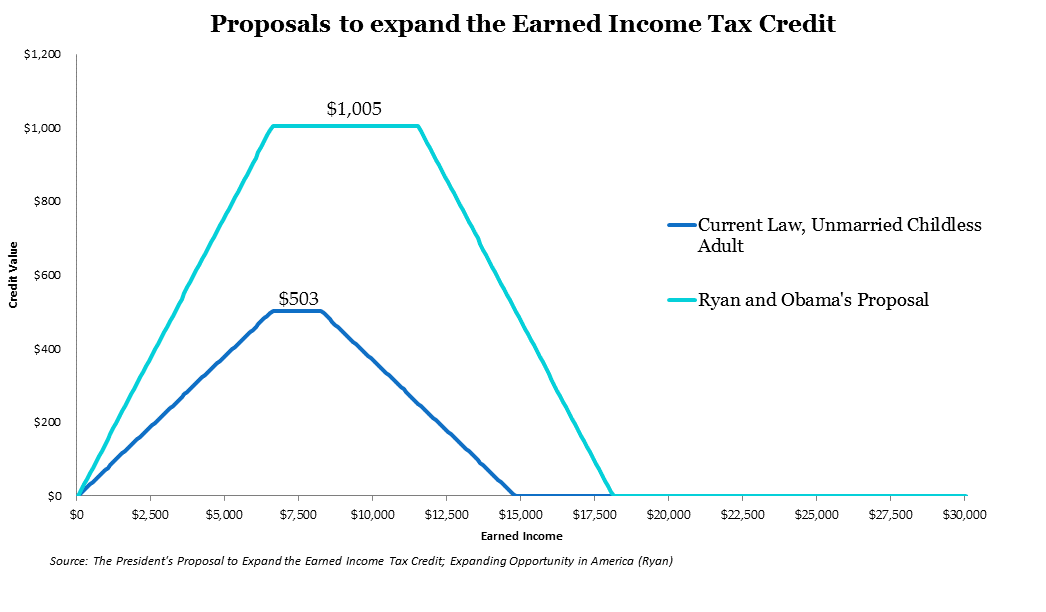
Created in 1975, the Earned Income Tax Credit is a refundable tax credit available to low income working Americans intended to both improve the lives of poor children and promote work. In keeping with these goals, families with more children are eligible for higher benefits and the credit increases as an individual’s earnings increase before plateauing and then tapering off.
Recently, there has been a growing consensus that we should expand the level of benefits available to childless workers – including a proposal from our own Isabel Sawhill. Obama and Ryan have presented proposals to expand EITC to childless workers with the express goal of targeting groups with low or declining workforce participation such as low-income, low-education men and women without children. Both proposals double the maximum credit for childless adults to around $1000 and increases the income level at which the benefit begins to around $18,000.
Budget or Spending Neutral: Paying for the EITC
Obama and Ryan take different approaches to funding the proposal. True to their party lines, Obama’s proposal is fiscally, but not spending neutral, whereas Ryan eschews higher tax rates in favor of cutting spending. Table 1 describes each plan’s funding proposal:
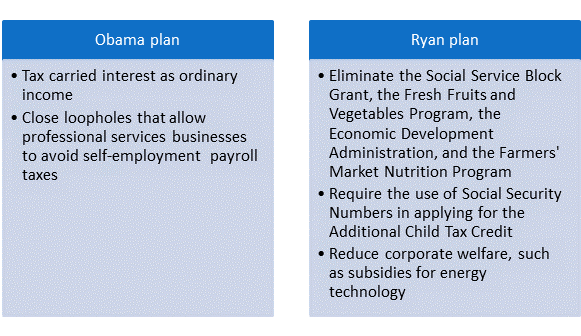 Funding President Obama’s EITC Expansion
Funding President Obama’s EITC Expansion
The first portion of Obama’s funding mechanism is taxing carried interest as ordinary income. What is carried interest? In short, managers of certain types of investment groups, such as private equity firms or hedge funds, are entitled a share of the profits of the investment fund in excess of the amount of capital they invest in the firm. That share, which makes up about one-third of the income that private equity general partners receive, is taxed at the lower rate assigned to capital gains.
Supporters of the current policy argue that carried interest should be treated similarly to capital gains from a non-managing partner’s financial investment in the firm. In contrast, supporters of reform say that carried interest represents compensation for services (i.e., managing the fund), not a return on investment and should thus be treated like a salary for tax purposes. For a more thorough explanation of the arguments for and against this proposal, see the Tax Policy Center’s explanation of carried interest.
This change in the tax system would mainly impact the so-called One-Percenters – the average salary for a hedge fund manager is around $2.2 million a year. Taxing carried interest like wage and salary income would raise about $15 billion in revenue over five years, according to the Joint Committee on Taxation.
The second part of Obama’s plan to fund the expansion of the EITC is to close a loophole in current tax law that allows individuals who own their own professional services business to avoid paying payroll taxes by classifying some of their income earnings as profits from pass‐through entities. This proposal is similar to one proposed by Senate Democrats which would require Americans with incomes over $250,000 a year who work in professional services firms, such as law, consulting, or lobbying, that derive over 75% of their profits from the service of 3 or fewer individuals to pay payroll taxes on all income from their partnership in that firm.
Funding Rep. Ryan’s EITC Expansion
The first portion of Ryan’s funding mechanism suggests cutting funding for the following programs, which he describes as “ineffective”:
| Table 1. Proposed budget cuts under Ryan’s Poverty Proposal | |
| Program | Purpose |
| Social Security Block Grant | Flexible funding source that allows states to allocate funds to vulnerable populations, primarily low- and moderate-income children and people who are elderly or disabled. Initiatives funded through SSBGs include daycare, health related services, substance abuse services, housing, and employment services. |
| Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Program | Initiative that provides free fresh fruits and vegetables to students in participating elementary schools during the school day with the goal of improving children’s diet and health by changing attitudes about healthy eating. |
| Economic Development Administration | Government agency that provides grants and technical assistance to economically distressed communities with the goal of attracting private investment in these communities and job creation. Example initiatives include the Public Works Program and the Trade Adjustment Assistance for Firms. |
| Farmers’ Market Nutrition Program | Part of the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children, commonly known as WIC. WIC provides supplemental foods, health care referrals and nutrition education at pregnant and post-partum women, infants, and children up to 5 years of age who are found to be at nutritional risk. FMNP specifically provides WIC participants with coupons to buy fresh fruits and vegetables at farmer’s markets |
Though Ryan describes these programs as ineffective, many of them provide valuable resources to the communities they serve. Take for example, the Social Services Block Grant: it supports state services that reach 23 million people, about half of whom are children. Republicans have argued that “many of the services funded by the SSBG are duplicative of other federal programs,” citing a Government Accountability Office report . But in fact, the GAO report makes no mention of SSBG other than to note that one area in which there are not enough federally funded programs to meet need is child care, an area in which SSBG is a key source of state funding. Eliminating SSBG would only increase this gap in funding.
The other programs Ryan proposes cutting, though smaller than SSBG in scope, have important impacts as well. An evaluation of FFVP by outside consultants finds that this program significantly increased children’s intake of fruits and vegetables (both in school and at home) and increased children’s positive attitudes towards fruits and vegetables and willingness to try new fruits and vegetables.
Ryan also proposes reducing fraud in the Additional Child Tax Credit by requiring the use of Social Security Numbers. Currently, individuals can use either a SSN or the individual tax identification number (ITIN) which is given to individuals who pay United States taxes but are not eligible to obtain a SSN, such as undocumented immigrants. Claims for the ACTC by ITIN filers amounted to about $4.2 billion in pay outs in fiscal year 2010 and enacting this proposal is estimated to reduce federal outlays by about 1 billion dollars each fiscal year.
House Republicans have repeatedly argued that having the IRS pay out tax credits to undocumented workers is fraud. They claim that children with undocumented parents should not receive benefits and that such credits encourage illegal immigration. But this is a misleading characterization and puts the burden of parents’ immigration choices on the shoulders of low-income children. Eligibility for the child credit is tied to the child, not the parent and requires documentation of the child’s citizenship or residency. 82 percent of the children whose parent files with an individual taxpayer identification number are citizens. Undocumented workers are not committing fraud by claiming this credit for U.S.-born or legally resident children of immigrant parents and requiring SSNs would likely result in benefits being taken away from low-income children.
Ryan’s final source of funding is a reduction in “corporate welfare” such as subsidies to corporations for politically favored energy technologies and the Department of Agriculture’s Market Access Program which subsidizes international advertising costs for agricultural companies.
Winners and Losers under Obama’s and Ryan’s EITC proposals
First, who benefits from expanding the EITC to childless workers? The Tax Policy Center’s analysis of the EITC proposal finds that those in the bottom quintile are most likely to benefit:
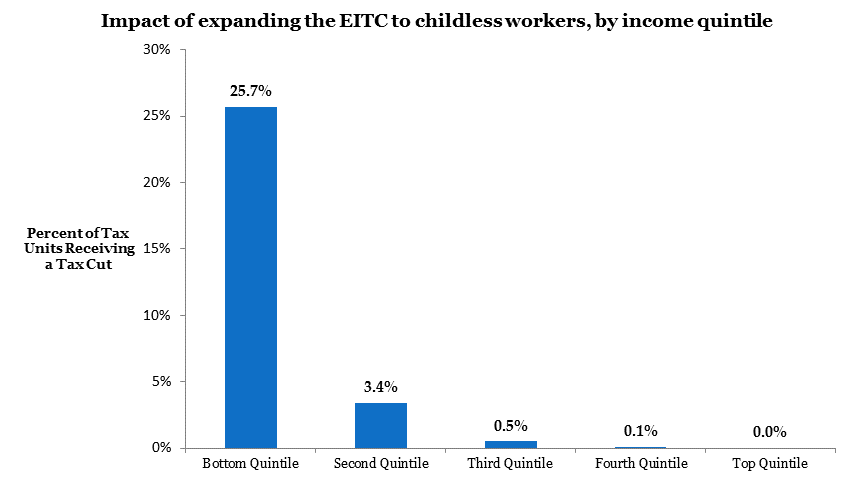
Source: Tax Policy Center, 2014
As the above graph shows, this tax credit is pretty successfully targeted at those who need the most help: about one-quarter of those in the bottom income quintile would have lower taxes under the proposed expansion, but very few tax payers in higher income quintiles see any impact.
Next, who is paying for this expansion? In the graph below, we show the groups most likely to be affected by the proposed funding mechanisms, broken down by income quintile. In some cases, the group described is not necessarily a perfect match for those affected: for example, not everyone who reports capital gains is a hedge fund manager reporting carried interest as capital gains. But these populations can still give us a sense of the distributional effects of, in order, taxing carried interest as ordinary income; closing tax loopholes for owners of S Corporations; cutting the Social Services Block Grant; cutting the Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Program; cutting the Farmers’ Market Nutrition Program; and requiring SSNs for the Additional Child Tax Credit.
The populations negatively affected by President Obama’s proposal are mostly concentrated among the top two income quintiles. For example, 75 percent of those reporting S Corporation profits are in the top two quintiles. In contrast, the populations negatively affected by Representative Ryan’s proposal are mostly concentrated in the bottom two quintiles.
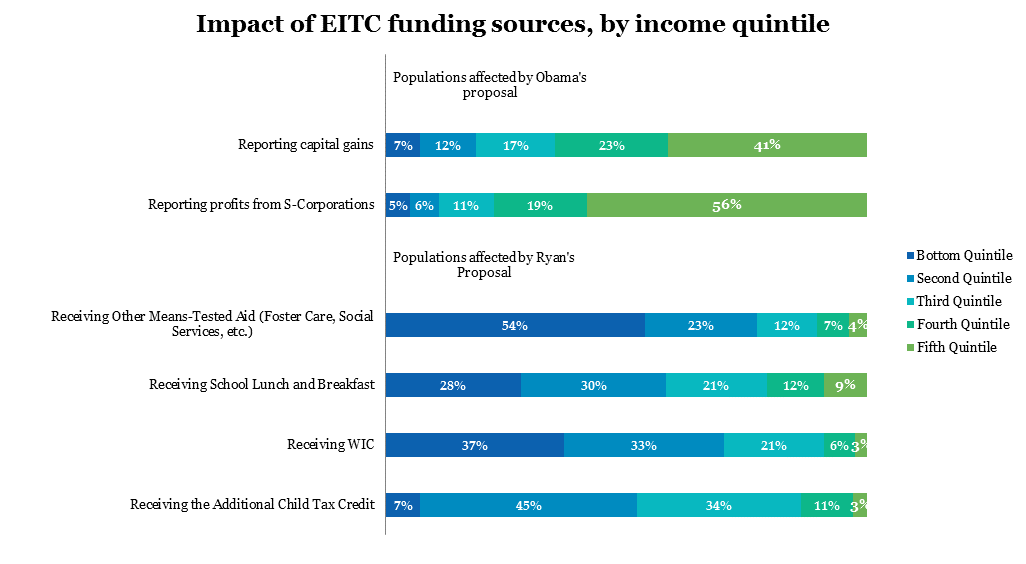
Source: For data on means-tested benefits: Rector and Kim, 2008; For data on S Corporations: Tax Policy Center, 2011; For data on capital gains: Tax Policy Center, 2014
Ryan’s EITC is pro-mobility…but funding it may not be
Paul Ryan seems to be thinking seriously about the issues of poverty and social mobility. He is a reformer as well as an authentic conservative.
While his willingness to embrace EITC expansion is welcome, his proposed funding methods raise serious questions. Paying for anti-poverty programs by cutting anti-poverty programs runs the risk of being self-defeating. No doubt some of them are not working as intended. But reform is the answer, rather than abolition. Many of these programs help those in the deepest poverty – who in many cases are those least likely to benefit from welfare-to-work policies such as the EITC, according to recent research from the Center for Budget and Policy Priorities and from the National Poverty Center.
Ryan’s package is worthy of serious attention, not least from the perspective of social mobility. It is important, however, not to consider the impact of the EITC expansion alone, but also how – and by whom- it will be paid for.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).





