EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
In November 2008, President George W. Bush convened the first G-20 summit in Washington to address the worst global financial economic crisis since the Great Depression. This summit provided a long-overdue opportunity for a dramatic and lasting change in global governance. This was followed by the election of Barack Obama, who had campaigned on a distinctly different foreign policy platform compared with his Republican rival, Senator John McCain. These two events were no mere coincidence.
The global crisis has moved the United States, along with the rest of the world, toward a new global economic order, with the G-20 summit as one of the principal manifestations of the new global governance system. Of course, movement toward this new economic arrangement and progress toward reformed global governance are not inevitable. It will take a clear and sustained commitment to a new set of values and strong leadership, especially from President Obama and the United States, to ensure that the G-20 summit is not a short-lived exception to what had been a long-standing stalemate in global governance reform. The effectiveness of the G-20 in addressing the global economic crisis could lay the foundation for a new global order and provide the impetus for the many other necessary global governance reforms. Whether or not this happens will depend to a significant extent on the direction chosen by President Obama.
The president’s vision of inclusion and openness and his approach to governing, which favors innovative and far-reaching pragmatic responses to key national and global challenges, make him a great candidate for this role. In due course the G-20 summit can also serve as a platform for addressing other pressing global issues, including trade, climate change, energy and food security and reform of global institutions. To achieve such an outcome, President Obama and other world leaders need to demonstrate a clear vision and strong leadership starting at the G-20 Summit in Pittsburgh and beyond.
“Old Economic Order” versus “New Economic Order”
From recent debates on foreign policy and global governance, we have identified two different perspectives or sets of principles underlying the approaches toward U.S. and global foreign policy. Table 1 summarizes the key elements of what we call the “Old Economic Order” in juxtaposition to the “New Economic Order.”
Table 1: Old versus New Economic Order
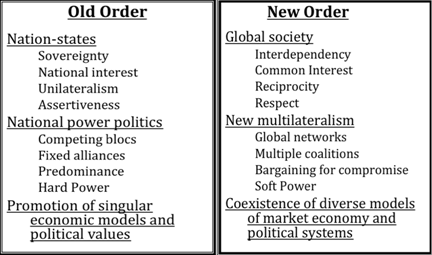
(Note: This table is adapted from one first presented by the authors in a seminar at the IMF in June 2007. See www.imf.org/external/np/seminars/eng/2007/glb/bl030607.pdf )
In the Old Order, the nation state is the point of departure, stressing the importance of sovereignty and national interest as the key principles driving a unilateral and assertive foreign policy. In contrast, the New Order’s starting point considers that we live in a global society, where interdependency and recognition of common interests are the key principles to be pursued in reciprocal relations and with mutual respect across borders. Under the Old Order the rules of national power politics prevail, as competing blocs and fixed alliances strive for predominance, with “hard power” if necessary. Instead, the New Order operates on the basis of a new multilateralism, which builds on the prevalence of global networks in all spheres of life and multiple coalitions across borders, where bargaining for compromise and the tools of “soft power” prevail. Finally, the Old Order promotes the notion that a single economic and political model should prevail, while the New Order accepts that different economic and political models coexist and compete side by side.
In the most simple terms, the Old Order broadly reflects the principles underlying the foreign policy agenda of the Bush administration and Senator John McCain’s presidential platform, while the New Order approximates those underpinning the platform of Senator Barack Obama’s presidential campaign and of his administration’s foreign policy stance. Key elements of the Old Order (except the last one) have also been attributed to the current foreign policy approach of Russia, while New Order principles can be ascribed to the European Union.
In fact, what is reflected in these two approaches is the difference between twentieth-century principles of foreign policy versus principles appropriate to today’s realities. We believe there are three interrelated sets of drivers of change that necessitate moving from the Old Order to the New Order. These drivers include the changing global demographic and economic balance, emerging global threats and the need for a more effective global governance system.
Drivers of Change
The first driver of change is the shifting global demographic and economic balance. By 2050, the world population is projected to reach 9.1 billion, up from 6.4 billion today, with the increase occurring almost entirely in today’s developing countries. China is widely predicted to be the largest economy in the early 2040s, with the U.S. economy in second place and India’s in third. Other emerging market economies, including Brazil, Indonesia and Russia, will be important economic players, while individual European countries will recede in importance. Continental Eurasia will be the new hub of global integration as China, India, Russia, the European Union and the Middle East’s energy-producing countries knit their economies ever closer together. The United States will remain a superpower, but only one among others. Together, the major world powers will have to confront the fact that people in poorer and weaker states will feel left behind. Simultaneously, cross-border networks—economic and political, public and private, elite and grassroots, legitimate and illegitimate—will continue to grow and will weaken the traditional hold states have over the economic, financial, social and political actions of their citizens. These networks will create bonds that will either reinforce or undermine global stability.
The second driver of change is a set of emerging global threats:
- The current financial and economic crisis—triggered by poor macroeconomic management and lax financial regulation—reflects the realities of long-term financial imbalances among key economies. It proves the difficulties of managing a highly interdependent global financial system in the absence of agreed-upon global financial surveillance, supervision and regulation. It is likely that risks of global financial stress will continue in the coming decades.
- Global disparities will increase as the rich and the rapidly growing economies do well, while many poor and stagnating countries are left behind. There is potential for rising disparities within countries, too. These inequities will reinforce risks of domestic and cross-border conflict and terrorism. At the same time, the United States and other industrialized countries face a progressive loss of traditional industries, jobs and wages. Aging populations and overburdened pension systems will challenge their fiscal stability and may lead to groundswells of anti-globalization sentiments.
- Rising food and energy prices, environmental threats and the risks of global epidemics—reinforced by population pressures—particularly affect the poorest countries.
- Growing global interdependencies across borders and sectoral lines mean that individual countries can no longer address these threats alone and that a global response has to be coordinated across sectors.
The third driver of change is the growing and widespread recognition that the current system of global governance has become increasingly fragmented, ineffective, outdated and resistant to change. This systemic weakness is reflected in the persistent stalemate on many of the pressing global issues—most notably the Doha trade round—but also on global poverty, climate change and the risk of pandemics. Moreover, global institutions have become unrepresentative in the face of the changed global economic and political balances. Hence their legitimacy is suffering badly, and yet there is stalemate in the reform of individual international organizations.
Together, these three factors have made the principles of the Old Order irrelevant and strongly point in the direction of a New Order. They represent the new reality for governments, citizens and international institutions and force them to adopt new principles and reform existing institutions.
While the drivers are strong and the new global reality is seemingly unassailable, change is not inevitable. Old habits die hard. In the United States, traditions of self-reliance and “exceptionalism” continue to shape Americans’ views of the rest of the world. At the same time, the widespread belief in the virtues of unfettered markets and low taxes, the influence of special interests for protection (agriculture, labor, old industry, banking) and the prevailing fractiousness of political decision-making may well undermine President Obama’s efforts to move toward a new global paradigm. Compounding the entrenchment of the Old Order, new nations that are still recovering from centuries of colonialism—facing economic and political instability and wishing to catch up with the successful industrial countries—are lured to a strong sovereign nation state, unfettered control over their borders and their citizens, and a confrontational approach to foreign policy. Even the much admired willingness of the Europeans to give up sovereignty in favor of supranational institutions has its limits, not least when it comes to giving up their prerogatives of dominating the governing boards of the international financial institutions and other global forums.
Leadership, conviction and persistence will be required among many actors on the global stage to ensure there is progress toward effective reform of global institutions. This potential for change is exemplified by the recent emergence of the G-20 summit as a vehicle for global governance.
The G-20 Summit—Origins, Options and Obstacles
Origins. The G-20 summit had its origins in the annual meetings of the G7—the leaders of a group of seven major Western industrial countries who gathered annually starting in the 1970s, initially to enhance economic and financial policy coordination in reaction to a major financial crisis. After the break-up of the Soviet Union, the G8 was formed by the addition of the Russian Federation. The G8 increasingly became preoccupied with global economic and political issues—in effect assuming the role of a global steering group. But widespread criticism began to mount about its role. The G8 summits were seen as ritualistic in process, ineffective in impact and increasingly unrepresentative in the face of global population and economic shifts, and hence lacking in legitimacy as a global steering group. The onset of the global financial crisis in mid-2008 pushed President George W. Bush into convening the G-20 Summit on November 15, 2008.
The ministerial-level G-20 was first created in the aftermath of the 1997-98 East Asia financial crisis. By convening representatives from 10 industrialized economies and 10 emerging market economies, the G-20 presented a much more geographically and culturally diverse group than the G8. With about 90 percent of the world’s economy and two thirds of the world’s population, the G-20 is also much more representative than the G8. Emerging market economies have been fully engaged in managing the proceedings of the meetings of G-20 finance ministers and central bank governors. It is therefore not surprising that there had been persistent calls by some experts and politicians for using the G-20 as a platform to replace the G8. While moving from G8 to G-20 summit might not create an optimal global steering group, it is a pragmatic and effective step, especially in response to crisis.
Options. Will the G-20 be a short-lived experiment or will it prove an effective tool of global governance? Various options are under debate among experts and practitioners. One possibility is to return to the G8 summits like the one Italy hosted in 2009 and Canada plans to host in 2010. There is concern that the G-20 format is too unwieldy for effective exchanges among the key players. Hence, there will be continuing debates about reducing the size of the summit to somewhere between thirteen and sixteen members, as reflected in the recent proposal by the French President, Nicolas Sarkozy, to create a G14. However, there are pressures to expand the number of participants to include more countries and to expand regional representation. Then there are proposals to develop a constituency-based approach to membership, with universal participation as in the case of the international financial institutions. Further, German Chancellor Angela Merkel and a United Nations Commission chaired by Nobel laureate Joseph Stiglitz propose to establish an Economic Security Council at the UN.
None of these options will likely materialize in the foreseeable future. Instead there are two probable outcomes: The first is the continuation of the G-20 summit with a gradually expanding mandate beyond the current crisis. For this to be successful, it is critical that the G-20 format proves its effectiveness in the coming months and years. This outcome has three requirements: that the number of participants does not expand; that participants focus on a limited number of action items; and that a small but effective secretariat is established to support and monitor the G-20 summit with logistics and technical expertise.
The most likely alternative to the G-20 summit is what is frequently referred to as “variable geometry.” Under this scenario, selected world leaders would convene on specific topics in shifting constellations, with participation of the most important actors decided separately for each topic. For example, the G-20 might continue to meet on global financial and economic matters for some time to come, while different groups would convene for action on climate change, nuclear proliferation or other topics. Support for this plan appears to be emerging from the Obama administration. It co-convened the summit on climate change at the tail-end of the 2009 G8 Summit, hosts the September 2009 G-20 economic summit in Pittsburgh and has called for a summit on nuclear non-proliferation in the spring of 2010. The challenge for summits of “variable geometry” is the ever-shifting number and composition of participants, the difficulty of systematic organization and follow-up and continuing debates about who would convene the summits, when, and with what participation.
Obstacles. As we look ahead, we see a number of challenges for the evolution of global summits beyond the G8, whether toward an effective G-20 or some alternative, especially summits of variable geometry. These challenges emanate from the diverging interests of four sets of players: the United States, Europe, the new emerging powers and the rest of the world.
For the foreseeable future, active U.S. leadership is needed to overcome inertia and collective action problems in addressing global challenges and breaking the stalemate in global governance reform. The Obama administration appears to strongly support a paradigm shift toward a new global order, but so far has not announced its position on summit modalities.
Europe is a key player and has proven a major obstacle to global governance reform as it continues to claim far too many chairs at the G-20 (and in other global forums and institutions) for its economic and demographic weight. In effect, Europeans can either retain their over-representation, which gives them a fragmented voice and weakens their influence while also weakening the global institutions; or they can bundle their votes, chairs and voice for greater impact and to ensure more effective international organizations. Unfortunately, the current stalemate on internal EU governance reform blocks any new European approach to global governance reform.
The new emerging powers, especially China, India and Brazil, will face the challenge of moving beyond their traditional role of the “excluded” and “representatives of the South.” They will need to accept co-responsibility for solving global problems and creating effective global governance institutions. They will have to look beyond issue-specific South-South coalitions to North-South coalitions where it is in their and the global interest (e.g., the push for international financial institution reform, for EU for consolidation, for the completion of the Doha Round, etc.). There are hopeful signs that this is beginning to happen. South Korea’s leadership of next year’s G-20 represents a critical test of whether the new powers are ready to participate and conduct a G-20 forum at the leaders’ level, not only ministerial.
Finally, there is the challenge of how to include the “excluded.” The G-20 is much more inclusive than the G8, but it still leaves out a majority of countries with a third of the world’s population. Options for associating the rest of the world with the summit include ad hoc outreach (as the G8 has done), expanding regional representation (as already practiced with the EU), introducing a constituency approach (as for the IFIs) and seeking a closer alignment with the UN (perhaps through an Economic Security Council). With the exception of the first two—which risk further expanding the number of participants at G-20 summits—none of the other options are likely to materialize soon. However, G-20 leaders will have to be sensitive to the needs of the “excluded” and ensure that the interests of the poorest countries are not neglected.
Conclusion
Great changes in the economic and political balance among countries, global threats and an antiquated global governance system confront the world community today. With the economic crisis as an immediate driver and a new U.S. president, the G-20 summit format has the potential to make a real shift in the global economic order in which a new set of values underpin the way countries and people cooperate across borders. To the extent that President Obama has articulated his vision of the global order and America’s role in it, we believe he is headed in the direction that stresses common interests in a global society, the need for multilateral action and understanding for alternative approaches to economic and political development. This is very promising. The effectiveness of the G-20 in addressing the global economic crisis could lay the foundation for a new global order and provide the impetus for the many other necessary global governance reforms.
However, Europe, China and India are also critical for progress. Moreover, if President Obama is believed to fail the test of competence at home or a major shock hits the United States, a reversal is possible in the U.S. In any case, significant changes in global governance will take time to transpire. We may well see a long period of transition with only gradual improvement in current institutions. In the meantime, pressures for increased regionalism, bilateral deals among the big players, geopolitical competition among power blocs and growing instability and threats from the “excluded” will undermine international cooperation and the whole idea of a global order.
The G-20 summit forum represents a great opportunity for world leaders to begin to put into action the principles of a new global order. It will allow them to address the immediate global financial and economic crisis in a collaborative spirit. And in due course the G-20 summit can also serve as a platform for addressing other pressing global issues, including trade, climate change, energy and food security, and reform of global institutions. To achieve such an outcome, President Obama and other world leaders need to demonstrate a clear vision and strong leadership at the G-20 Summit in Pittsburgh and beyond.




