In his state of the union and his budget, the President spoke of the stagnation of middle class incomes. Whatever growth we have had has not been broadly shared. More than 78% of the growth in GDP between 1979 and 2013 has gone to the top one percent. Even Republicans are beginning to worry about this issue although they have yet to develop concrete proposals to address it.
Slow Growth in Incomes
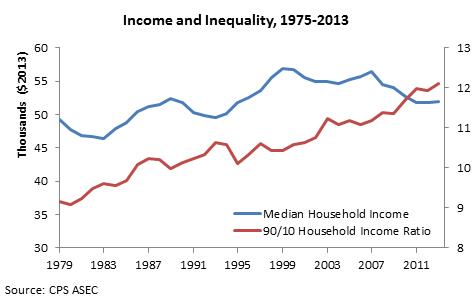
Middle class incomes were growing slowly before the recession and have actually declined over the past decade. In addition, according to the New York Times, the proportion of the population with incomes between $35,000 and $100,000 in inflation-adjusted terms fell from 53% in 1967 to 43% in 2013. During the first four decades this was primarily because more people were moving into higher income groups, but more recently it was because they have moved down the ladder, not up. One can define the middle class in many different ways or torture the data in various ways, but there is plenty of evidence that we have a problem.
What to Do
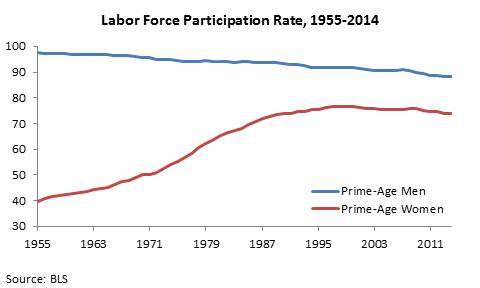
The most promising approach is what I call “the second earner solution.” For many decades now, the labor force participation rate of prime age men has been falling while that of women has been rising. The entry of so many women into the labor force was the major force propelling whatever growth in middle class incomes occurred up until about 2000. That growth in women’s work has now levelled off. Getting it back on an upward track would do more than any policy I can think of to help the middle class.
Imagine a household with one earner making the average wage of today’s worker and spending full-time in the job market. That household will have an income of around $34,000. But if he (or she) has a spouse making a similar amount, the household’s income will double to $68,000. That is why the President’s focus on a second-earner credit of $500, a tripling of the child care tax credit, expanding the Earned Income Tax Credit, and providing paid leave are so important. These policies are all pro-work and research shows they would increase employment.
No Marriage = No Second Earner
One problem, of course, is that fewer and fewer households contain two potential workers. So it would also help to bring back marriage or at least its first cousin, a stable cohabiting relationship. My ideas on this front are spelled out in my new book, Generation Unbound. In a nutshell, we need to empower women to not have children before they have found a committed partner with whom to raise children in a stable, two-parent family. Whatever the other benefits of two parents, they have twice as much time and potentially twice as much income.
Other Needed Responses
Shouldn’t we also worry about the wages or the employment of men? Of course. But an increase in, say, the minimum wage or a better collective bargaining environment or more job training will have far smaller effects than “the second earner solution.” In addition, the decline in male employment is related to still more difficult problems such as high rates of incarceration and the failure of men to take advantage of postsecondary education as much as women have.
Still the two-earner solution should not be pursued in isolation. In the short-term, a stronger recovery from the recession is needed and in the longer-term, more effective investments in education, research, infrastructure, and in labor market institutions that produce more widely-shared growth, as argued by the Commission on Inclusive Prosperity. But do we really expect families to wait for these long-term policies to pay off? It could be decades.
In the meantime, the President’s proposals to make work more appealing to existing or potential second earners deserves more attention.



Commentary
Op-edHow Second Earners Can Rescue the Middle Class from Stagnant Incomes
February 10, 2015