Baltimore police officer Edward Nero, one of six being tried separately in relation to the arrest and death of Freddie Gray, has been acquitted on all counts. The outcome for officer Nero was widely expected, but officials are nonetheless aware of the level of frustration and anger that remains in the city. Mayor Stephanie Rawlings Blake said: “We once again ask the citizens to be patient and to allow the entire process to come to a conclusion.”
Since Baltimore came to national attention, Brookings scholars have probed the city’s challenges and opportunities, as well addressing broader questions of place, race and opportunity.
- In this podcast, Jennifer Vey describes how, for parts of Baltimore, economic growth has been largely a spectator sport: “1/5 people in Baltimore lives in a neighborhood of extreme poverty, and yet these communities are located in a relatively affluent metro area, in a city with many vibrant and growing neighborhoods.”
-
Vey and her colleague Alan Berube, in this piece on the “Two Baltimores,” reinforce the point about the distribution of economic opportunity and resources in the city:
In 2013, 40,000 Baltimore households earned at least $100,000. Compare that to Milwaukee, a similar-sized city where only half as many households have such high incomes. As our analysis uncovered, jobs in Baltimore pay about $7,000 more on average than those nationally. The increasing presence of high-earning households and good jobs in Baltimore City helps explain why, as the piece itself notes, the city’s bond rating has improved and property values are rising at a healthy clip.”
- Groundbreaking work by Raj Chetty, which we summarized here, shows that Baltimore City is the worst place for a boy to grow up in the U.S. in terms of their likely adult earnings:
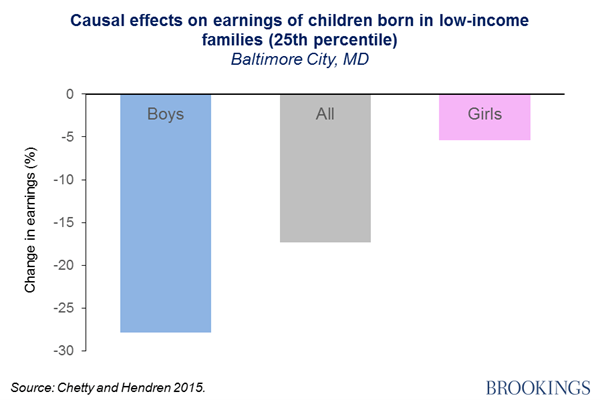
- Here Amy Liu offered some advice to the new mayor of the city: “I commend the much-needed focus on equity but…the mayoral candidates should not lose sight of another critical piece of the equity equation: economic growth.”
- Following an event focused on race, place and opportunity, in this piece I drew out “Six policies to improve social mobility,” including better targeting of housing vouchers, more incentives to build affordable homes in better-off neighborhoods, and looser zoning restrictions.
- Frederick C. Harris assessed President Obama’s initiative to help young men of color, “My Brother’s Keeper,” praising many policy shifts and calling for a renewed focus on social capital and educational access. But Harris also warned that rhetoric counts and that a priority for policymakers is to “challenge some misconceptions about the shortcomings of black men, which have become a part of the negative public discourse.”
- Malcolm Sparrow has a Brookings book on policing reform, “Handcuffed: What Holds Policing Back, and the Keys to Reform” (there is a selection here on Medium). Sparrow writes:
Citizens of any mature democracy can expect and should demand police services that are responsive to their needs, tolerant of diversity, and skillful in unraveling and tackling crime and other community problems. They should expect and demand that police officers are decent, courteous, humane, sparing and skillful in the use of force, respectful of citizens’ rights, disciplined, and professional. These are ordinary, reasonable expectations.”
Five more police officers await their verdicts. But the city of Baltimore should not have to wait much longer for stronger governance, and more inclusive growth.


Commentary
After second verdict in Freddie Gray case, Baltimore’s economic challenges remain
May 23, 2016