The housing policy matchmaker
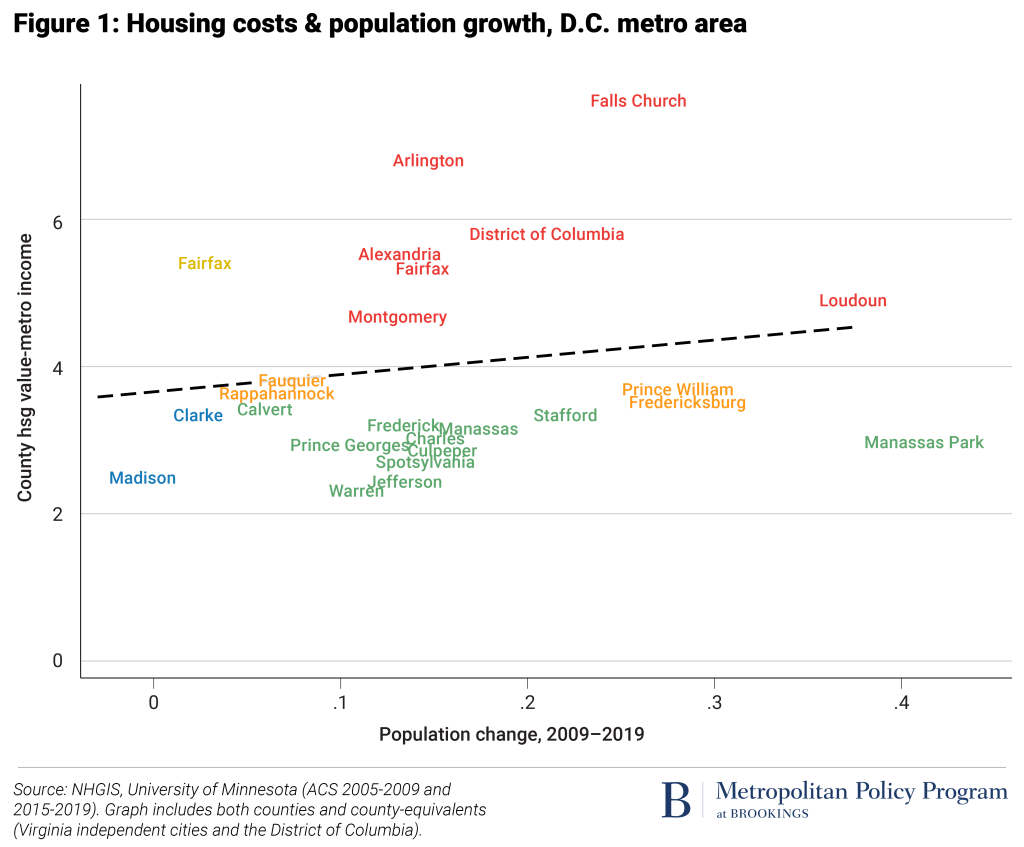
Loudoun County is rapidly growing, high-priced county located in a growing, high-priced metropolitan area (Washington, D.C.). All but one of the metro area’s 25 jurisdictions saw positive population growth from 2009 to 2019, and eight jurisdictions fall into the highest cost category (housing value-to-income ratios over 4). Loudoun had the second highest population growth rate in the metro area (0.25).
To develop a more complete picture of housing market conditions in Loudoun County, we draw on a broader set of measures that capture demand, affordability of both owner-occupied and rental housing, and housing quality (Table 1).

Key findings from this comparison are:
- Loudoun County’s population growth rate, 0.35, is more than double that of the average county in the D.C. metro area, and well above the national average. Fast population growth drives the demand for additional housing.
- The typical household in the Washington D.C. metro area would have to pay 4.9 times their annual income to purchase the median home in Loudoun County. Home value-to-income ratios between 2.5-3.5 are considered healthy.
- Households earning less than $74,800 (or 78% of the metro area median income) would have difficulty paying rent for the median rental home in Loudoun County, while spending no more than 30% of their income on rent. While most middle-income households in the metro area can afford median rent in Loudoun, most low- and moderate-income households in the region will fall below this threshold.
- 20.2% of renters in Loudoun County are severely cost burdened, meaning they spend more than half their income on rent. That is slightly below the severely cost-burdened share for the entire D.C. metro area and below the national average.
- The vacancy rate, 3.3%, is very low. Vacancy rates of 6-10% are considered healthy. Low vacancy rates are an indication that supply is not keeping up with demand.
- The housing stock is quite new relative to the region and country: only 2.8% of homes were built prior to 1940, while 72.6% were built after 1990. New housing is generally higher quality than older homes and more expensive to buy or rent, while having lower maintenance costs.
Recommended policy solutions
Increase housing supply. Housing is expensive because supply has not kept up with demand. High prices and rents, combined with low vacancy rates, indicate that there is unmet demand for housing. It is important to realize that no single county can produce enough housing to meet demand for the entire metro area. Reducing housing costs in expensive, supply-constrained metro areas will require sustained periods of increased housing production across multiple jurisdictions. All high-cost counties within a metro area adopting the strategies described below will have better results than actions by a single county, and county officials can play a leading role in coordinating across jurisdictions and sectors to achieve those goals.
Make it easier to build small, moderately-priced homes. In expensive metro areas, the size of homes and the amount of land used per home are major factors in the price of individual homes. Single-family detached homes on large lots are the most expensive structure type. Rowhouses, townhomes, two-to-four family homes, and low-rise apartment buildings have lower per-unit development costs than detached homes. These structures are also well suited for rental housing, which is more affordable to moderate-income households, and as “starter homes” for prospective first-time buyers who are currently priced out of the market. Zoning changes that enable smaller, less land-intensive structures to be built as-of-right in more parts of the county will increase the diversity of housing choices and widen the price range of available homes. Companion zoning reforms include relaxing dimensional requirements, such as minimum lot sizes, setbacks, lot coverage, or floor-to-area ratios. Reducing minimum parking requirements and allowing flexibility in design standards can also result in cost savings for newly built homes.
Developing a specific menu of zoning reforms will require an assessment of the county’s current housing types, density, and land availability. Exactly what types of zoning reform will yield the largest supply increases and cost reductions will vary across high-cost counties. A locality that has predominantly detached homes on one-acre lots—typical of many outer suburbs—could realize substantial cost savings by allowing rowhouses on 4,000 square foot lots. For urban counties and inner-ring suburbs that currently have many small-lot homes and little undeveloped land, increasing housing supply may require zoning reforms that allow redeveloping single-family homes, parking lots, or commercial buildings as low- or mid-rise apartments. High-rise construction has the highest per-square-foot costs, and will typically only occur in places with very expensive land and high rents.
Make the development process simpler and shorter. The length of time required to complete development projects, combined with the complexity of the process, are significant factors in the price of newly built housing. Local development processes that make decisions on a case-by-case basis, rather than following consistent, transparent rules, increase the uncertainty and risk of development, which translates into higher costs. Discretionary processes include requiring special permits (also called conditional use permits), site plan reviews, environmental impact reviews, and negotiations over impact fees all add to development costs. Policy changes that reduce development time and complexity include allowing more development as-of-right; integrating approvals for multiple parts of the development process through a one-stop-shopping approach; setting a clear and transparent impact fee schedule; and setting deadlines that require decisions to be made within a set period of time.
Expand vouchers or income supports for low-income renters. Even in communities where enough housing is built to accommodate increased demand, market-rate housing remains unaffordable to many low-income households. The poorest 20% of households everywhere in the U.S. spend more than half their income on housing, well above the threshold HUD defines as affordable. Only one in four eligible households receives federal rental assistance, including vouchers and public housing. Local governments that have sufficient resources can supplement these programs through locally funded rental vouchers or direct income supports. These programs require an ongoing funding source; high-income counties may be able to finance local vouchers from general tax revenues such as property or sales taxes, while lower-income counties will require support from state or federal governments.
An alternative to household-based subsidies for low-income households is to provide land or financial support for acquisition or construction of affordable housing. Local jurisdictions often own or have significant control over physical assets—such as publicly owned land or airspace—that can be leveraged to increase the availability of affordable housing in the community. Affordable housing trust funds are a flexible financing vehicle to support these activities.
Housing market conditions can vary across submarkets within counties. These policy recommendations are based on an assessment of overall county-level housing metrics. Larger counties often have multiple distinct submarkets with varying affordability, physical quality, infrastructure availability, and development regulations. Cities, towns, and neighborhoods that offer the best economic opportunity—proximity to well-paid jobs, transportation, good schools, and other amenities—often have housing that is too expensive for moderate-income households in the county. Lower-cost communities tend to have older, poorer quality housing. Addressing within-county disparities in housing costs, availability, and quality may require coordinating between independent political entities (e.g., separate cities and towns) in counties with more fragmented local government.
